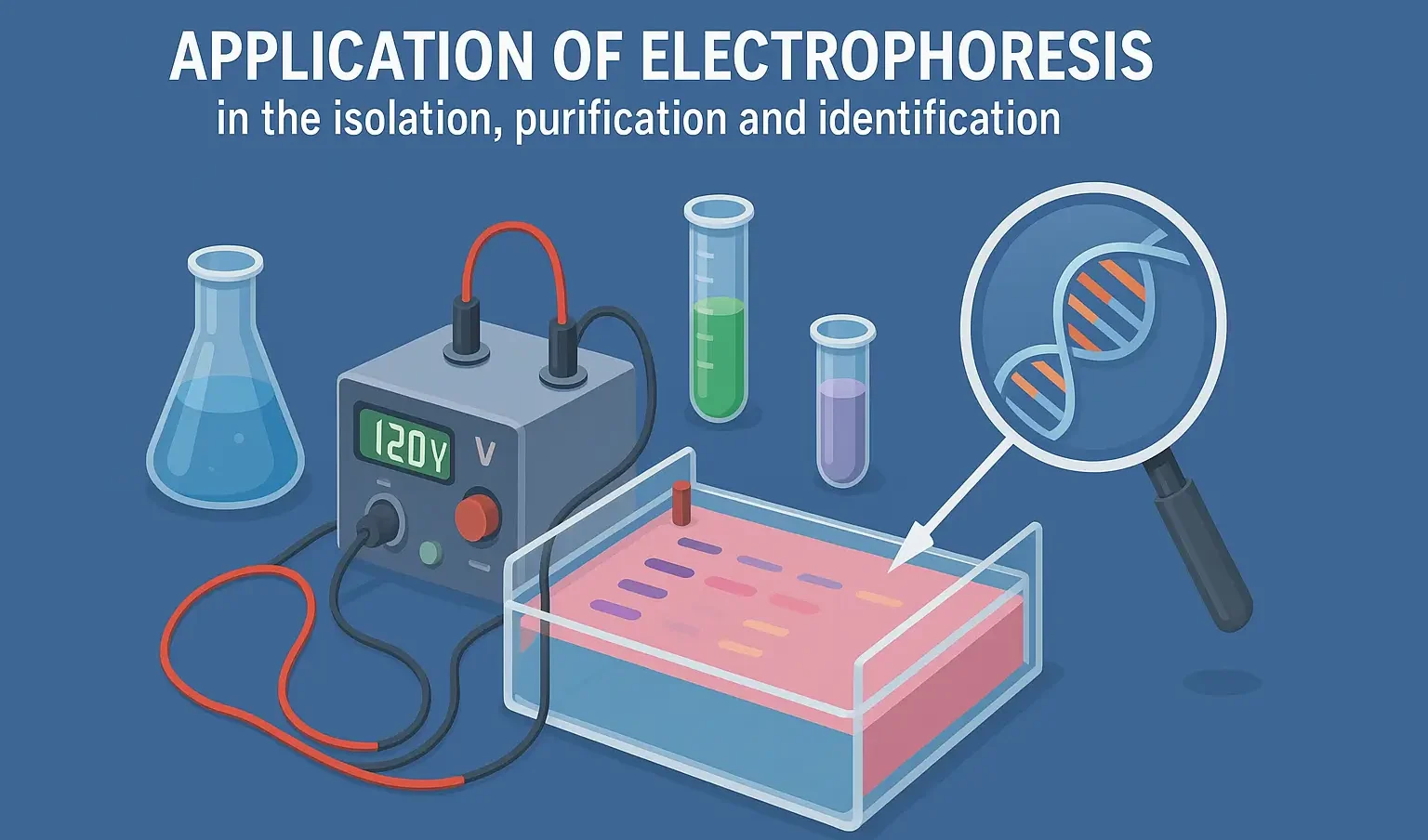
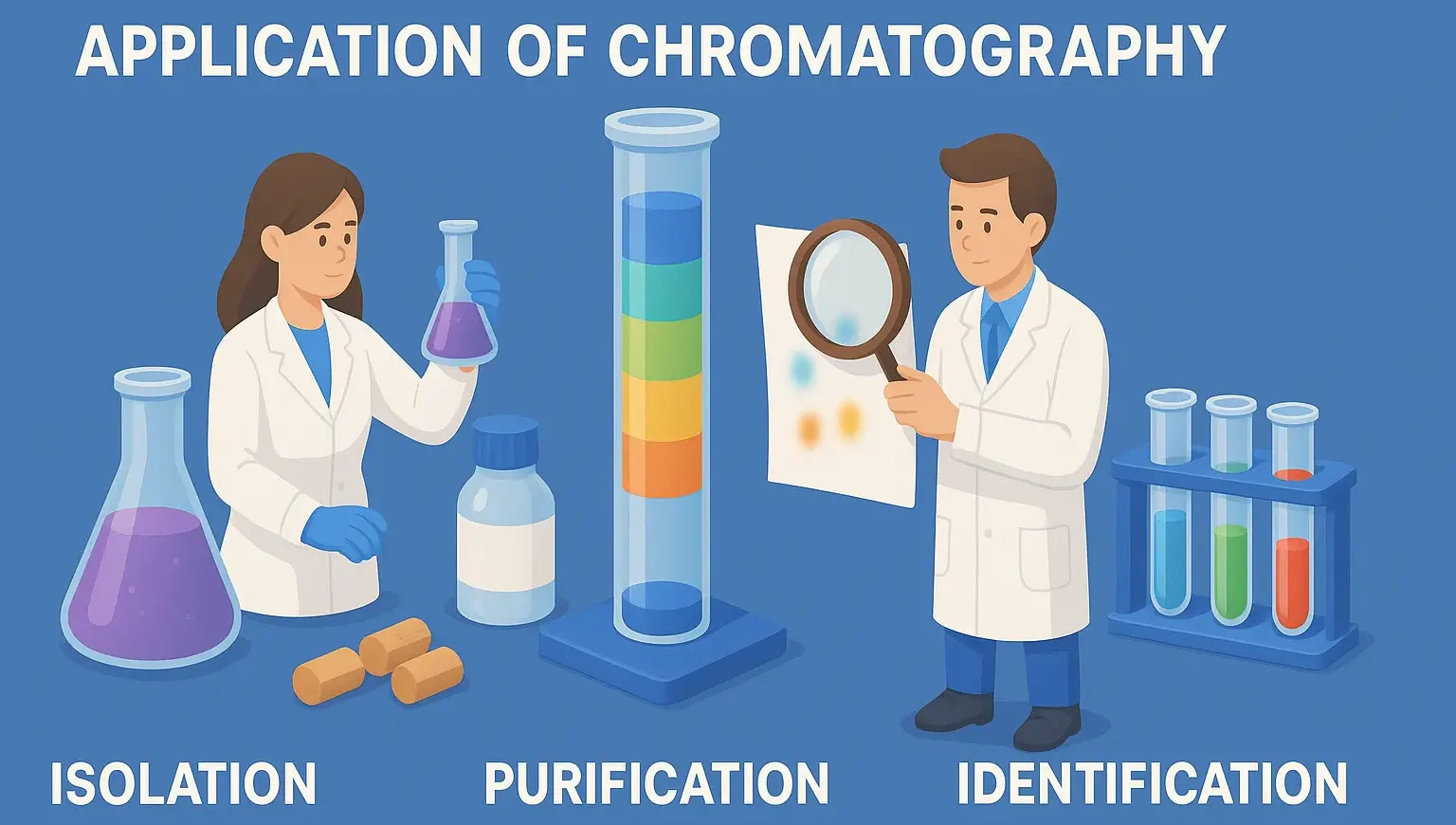
Processing of Medicinal Plants
Processing of Medicinal Plants involves cleaning, drying, and preserving plant materials for medicinal use. Processing involves post-harvest handling of medicinal plants to maintain their potency, stability, and purity. Steps in Processing Cleaning Removes dirt, dust, and foreign materials. Washing (if needed) – Aloe vera gel is extracted after thorough washing. Drying Reduces moisture content to … Read more