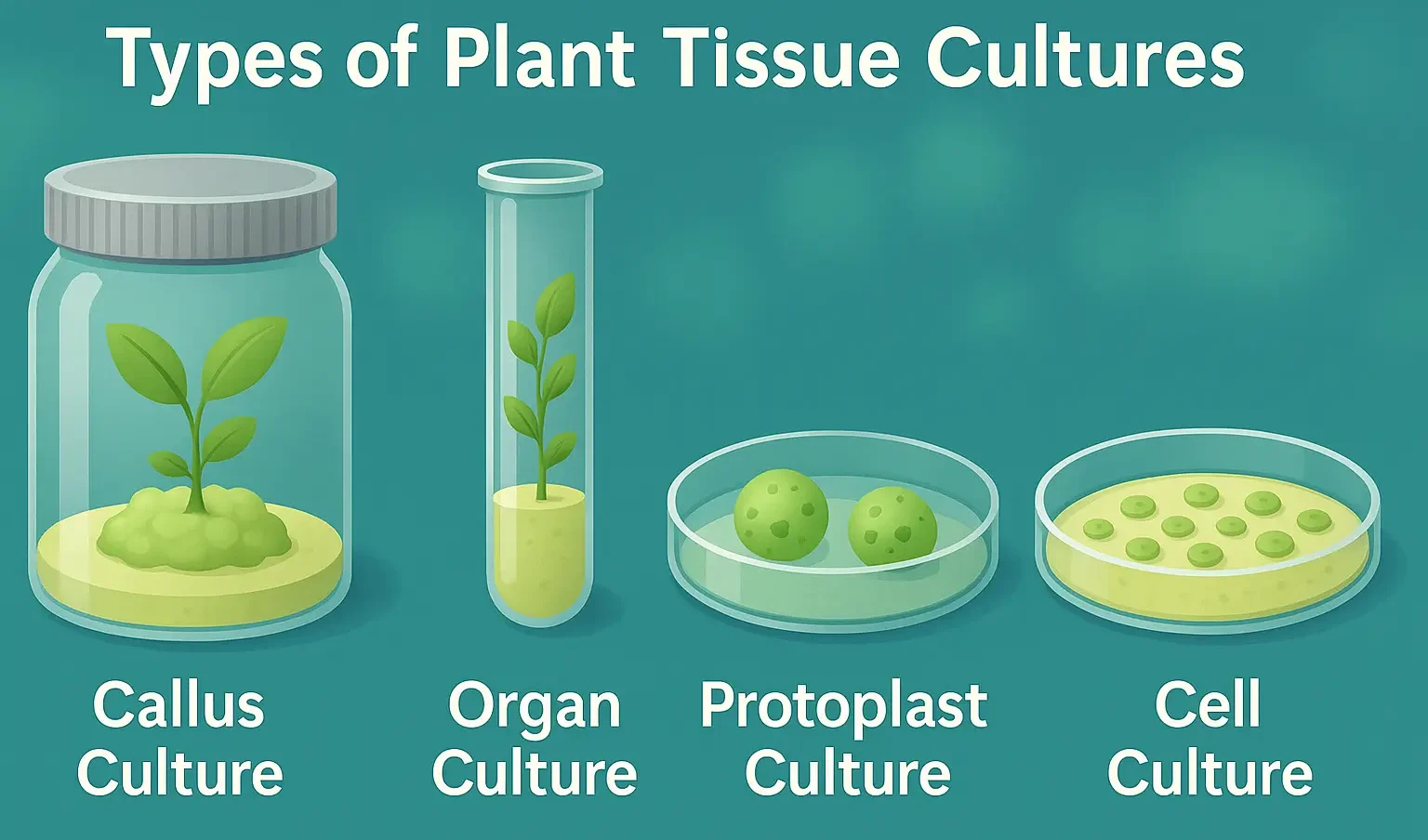
Edible Vaccines
What Are Edible Vaccines? Edible vaccines are genetically modified plants that produce antigens, which, when consumed, stimulate an immune response against specific diseases. How Are They Made? A gene encoding an antigen (from a virus or bacterium) is inserted into a plant’s DNA using Agrobacterium tumefaciens or gene gun technology. The plant expresses the antigen, … Read more