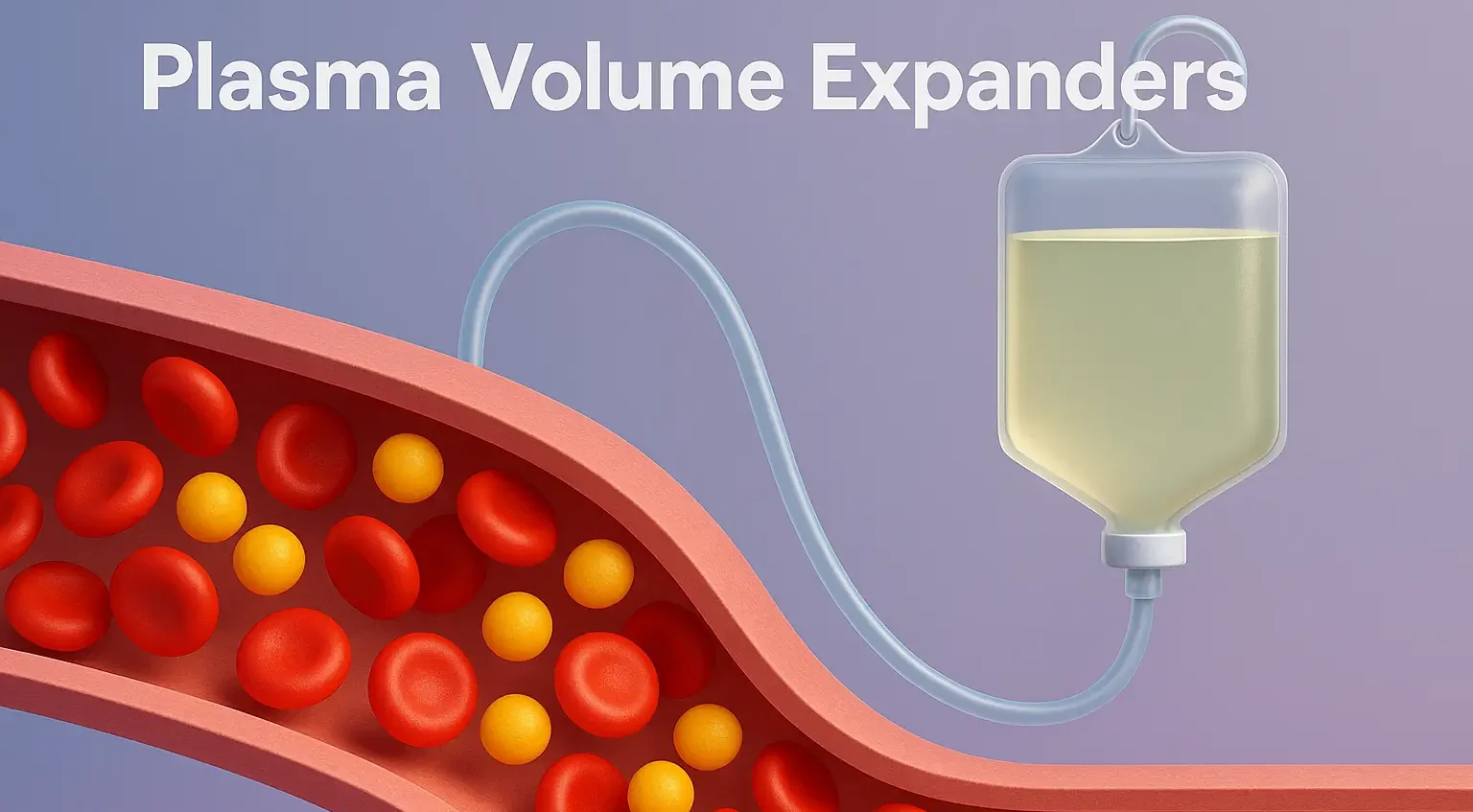
Plasma Volume Expanders
Definition of Plasma Volume Expanders Plasma Volume Expanders are fluids used to restore and maintain intravascular volume in patients experiencing hypovolemia (low blood volume), such as during shock, trauma, burns, or surgery. They work by increasing osmotic pressure, which helps retain fluid within the vascular compartment. Types of Plasma Volume Expanders: 1. Crystalloids: Normal Saline … Read more