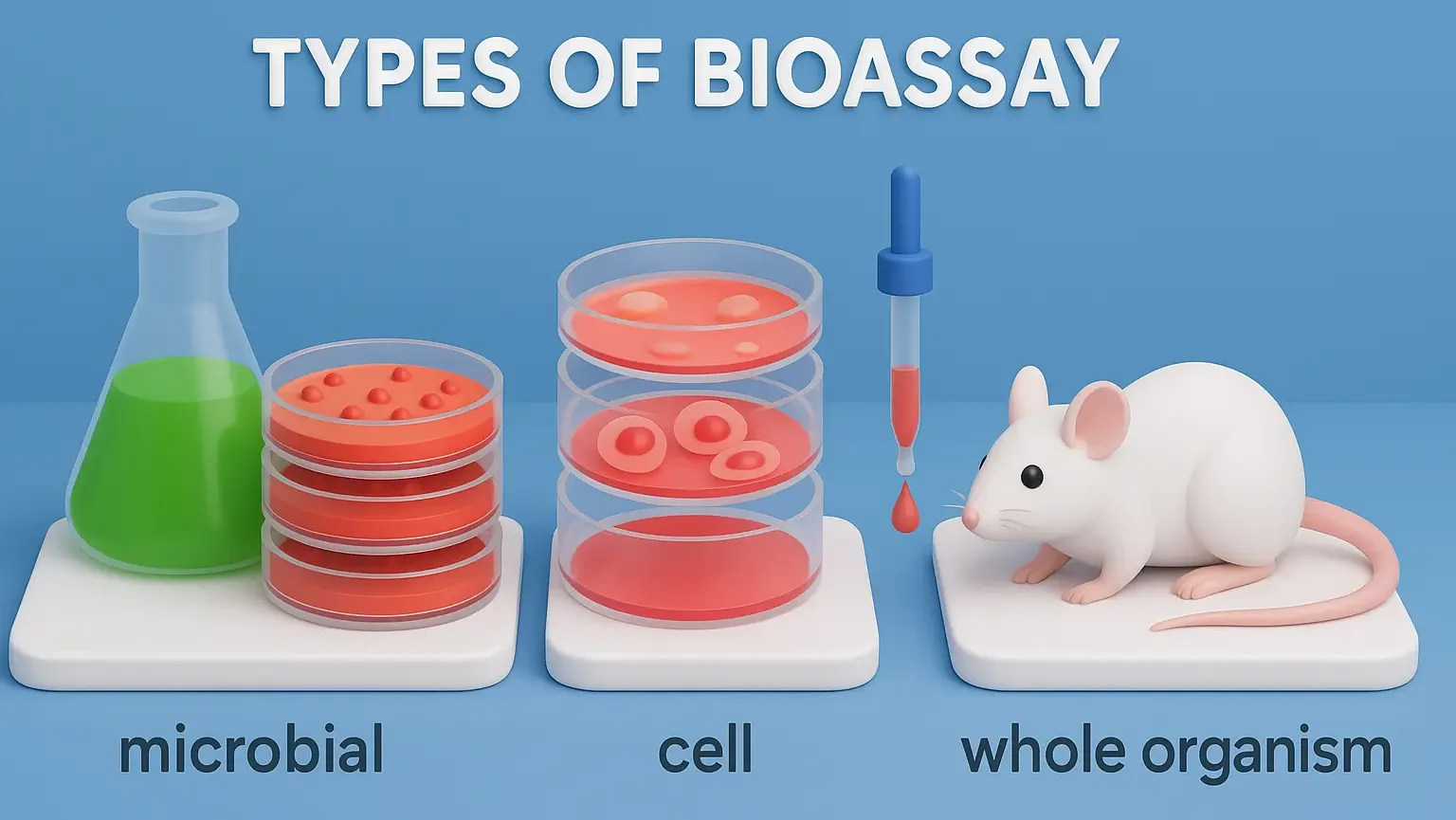
Types of Bioassay
Types of Bioassay: Include quantal, graded, and endpoint assays to measure drug effects. Types of Bioassay: Used to determine potency, efficacy, and standardization of drugs. Bioassays can be broadly classified based on the nature of the biological system used and the type of response measured. Types of Bioassay Graded Response Bioassay Measures the intensity of … Read more