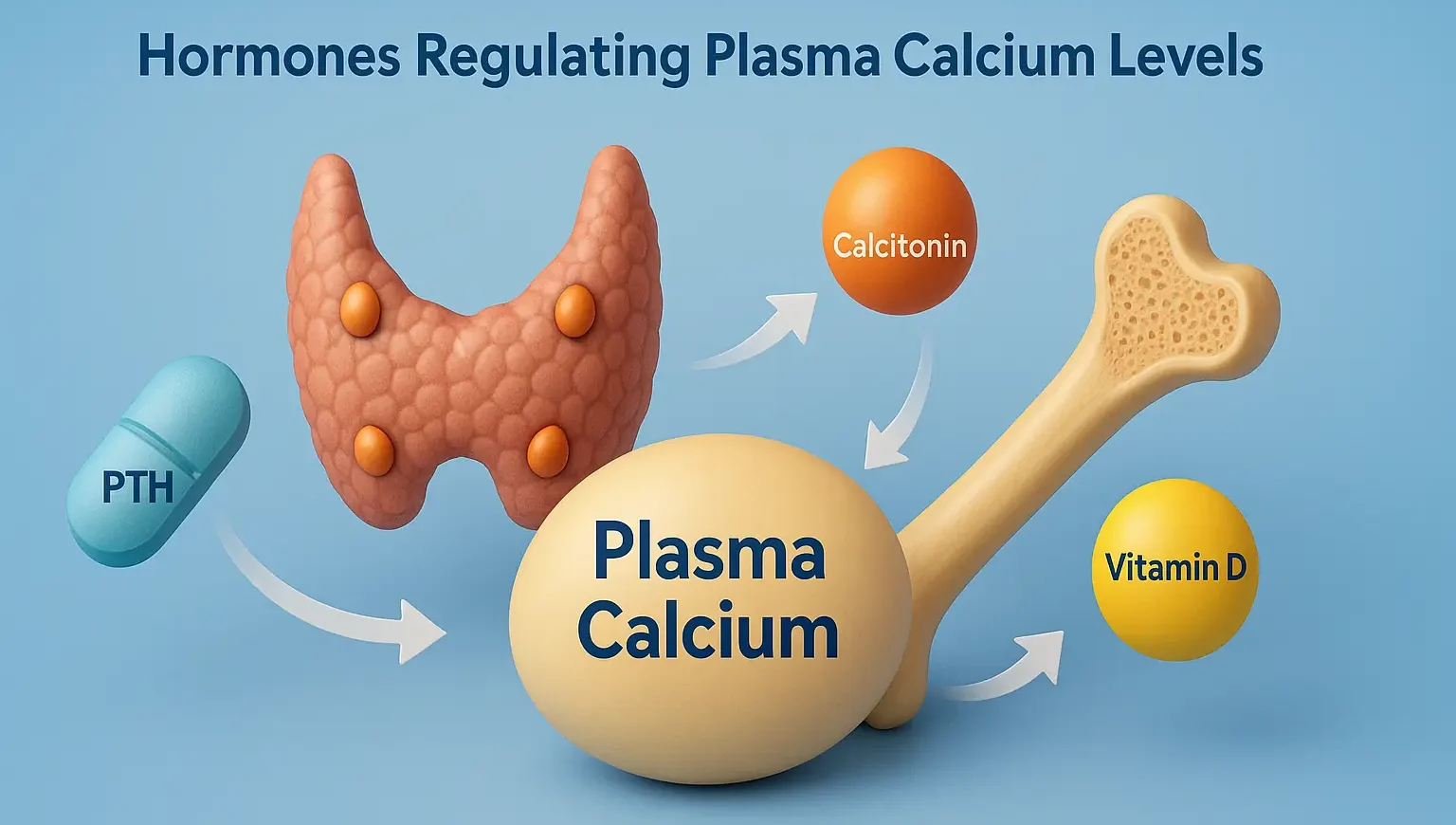
Glucagon
Glucagon: A peptide hormone that raises blood glucose by stimulating glycogen breakdown in the liver. Glucagon: Used in emergency treatment of severe hypoglycemia and as a diagnostic aid. Physiology: Secreted by α-cells of the pancreas in response to low blood glucose. Increases blood glucose by stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver. Glucagons (e.g., glucagon … Read more