Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents (NSAIDs)
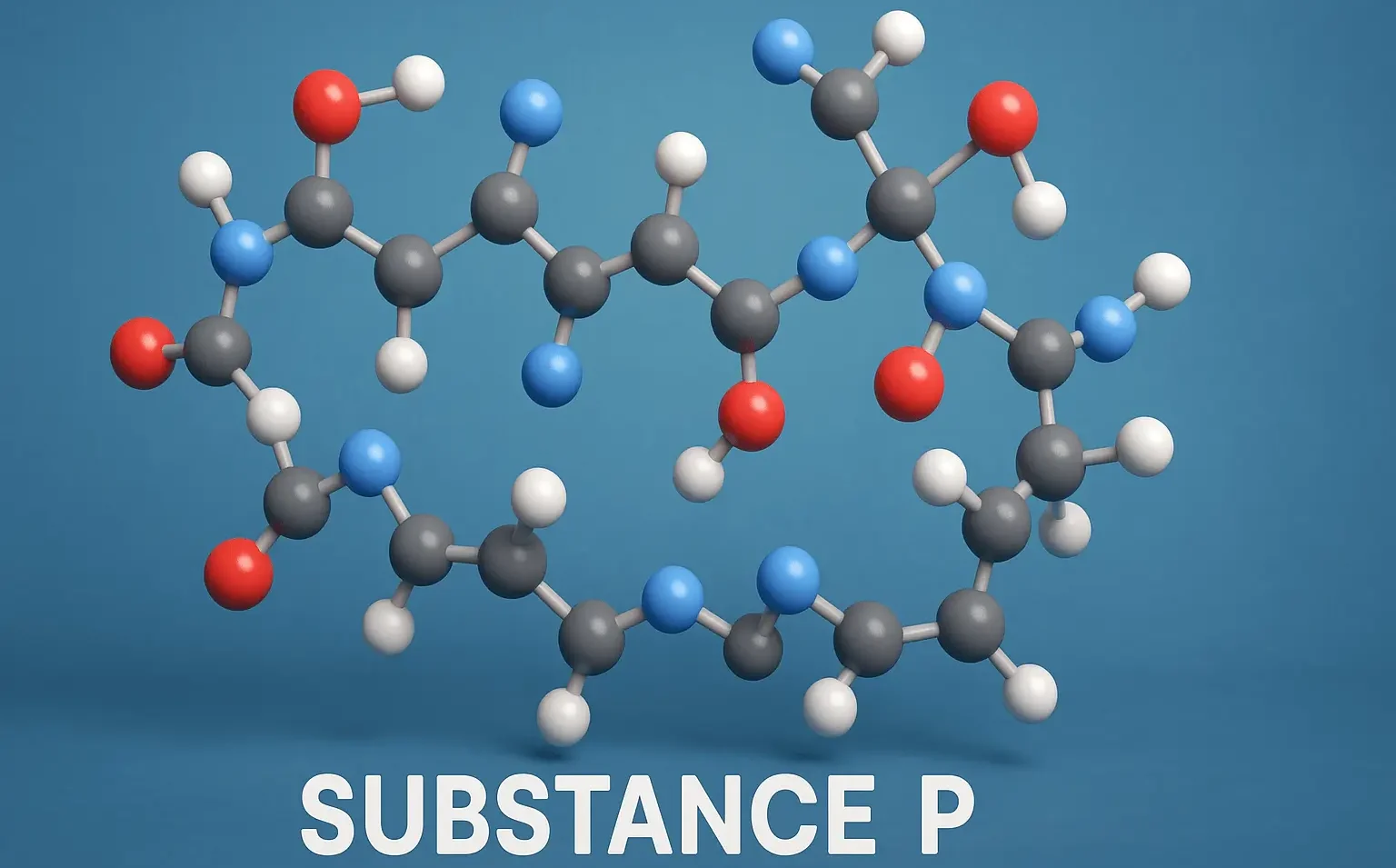
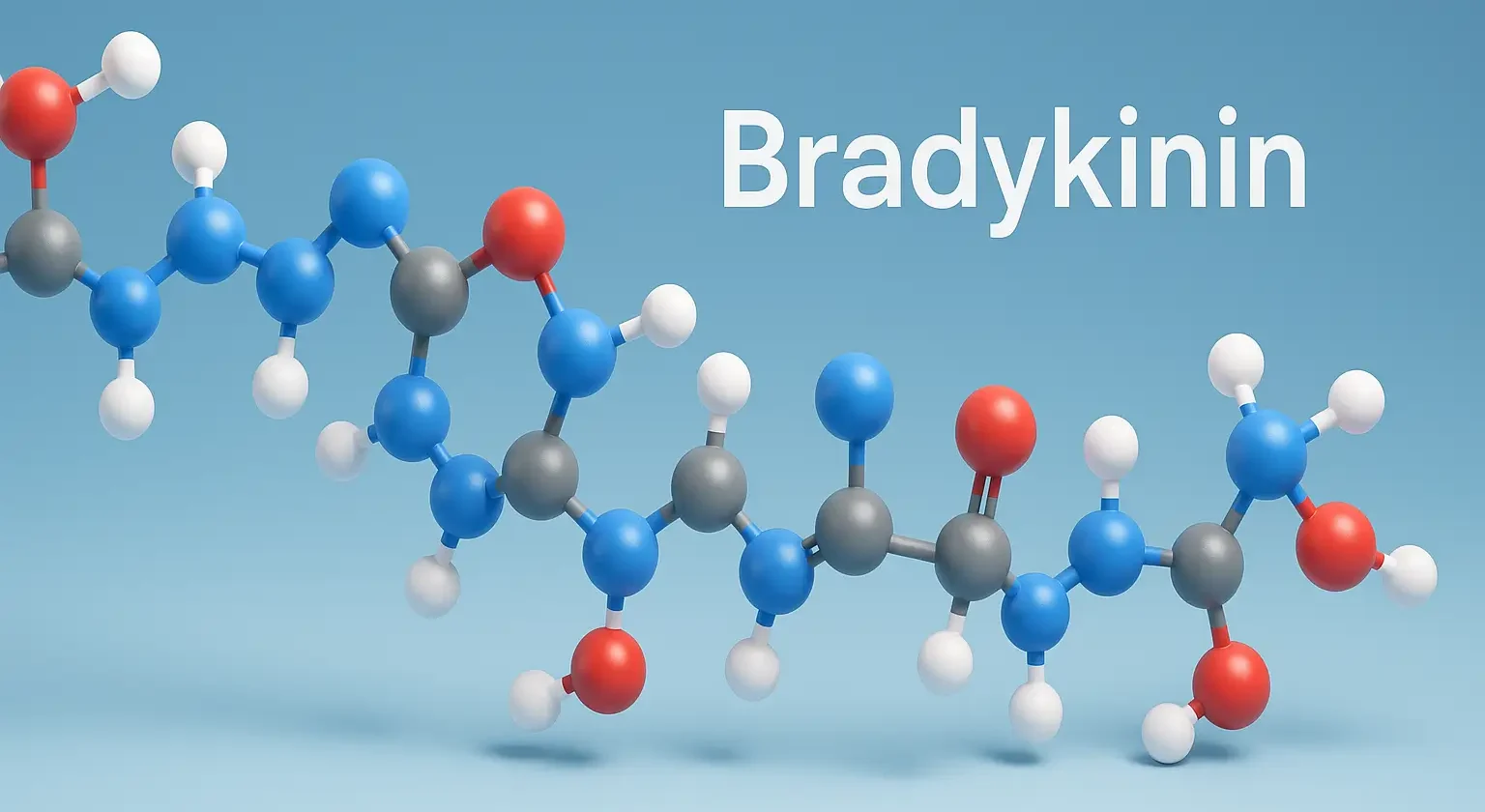
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents (NSAIDs) are a class of medications widely used for their analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory properties. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents (NSAIDs) inhibit COX enzymes to block prostaglandin synthesis. They are termed “non-steroidal” to distinguish them from corticosteroids, which are another major class of anti-inflammatory drugs. Therapeutic Effects: Analgesic Antipyretic Anti-inflammatory Mechanism of Action NSAIDs … Read more