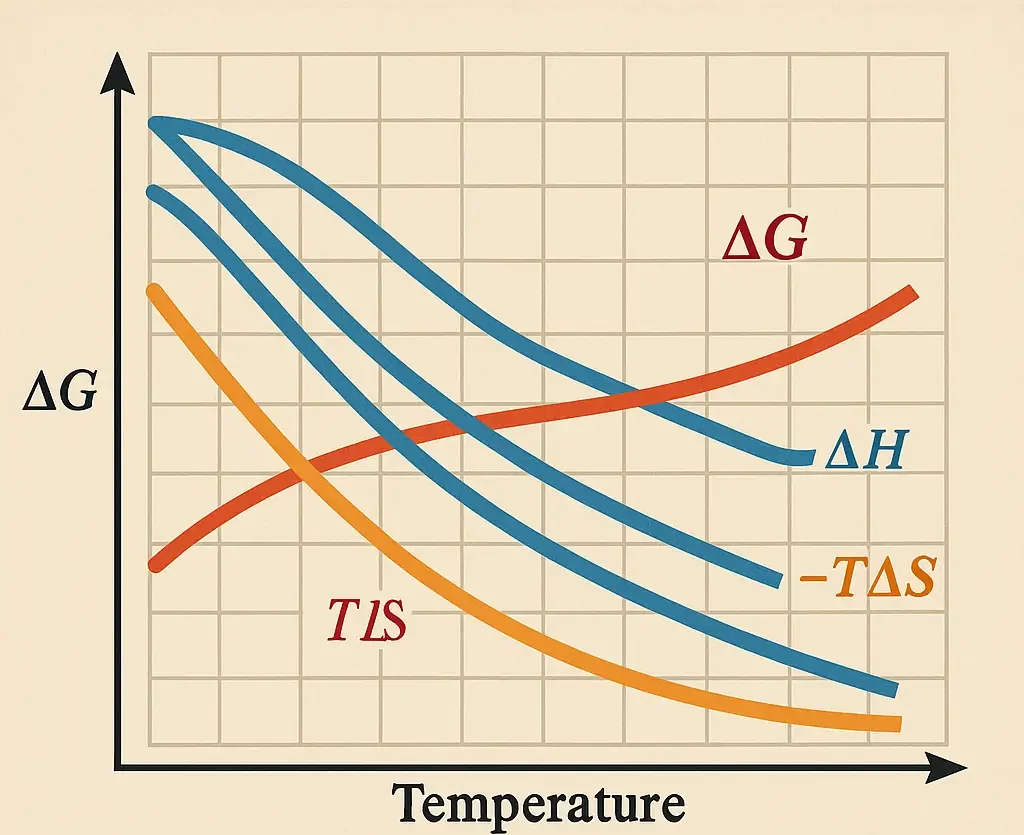
Buffers
Definition of Buffers They are temporary memory storage areas that hold data while it is being transferred between two locations or processes. Buffer Solution: A system that minimizes changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. Components: Weak Acid and its Conjugate Base (e.g., acetic acid and sodium acetate). Weak Base and … Read more