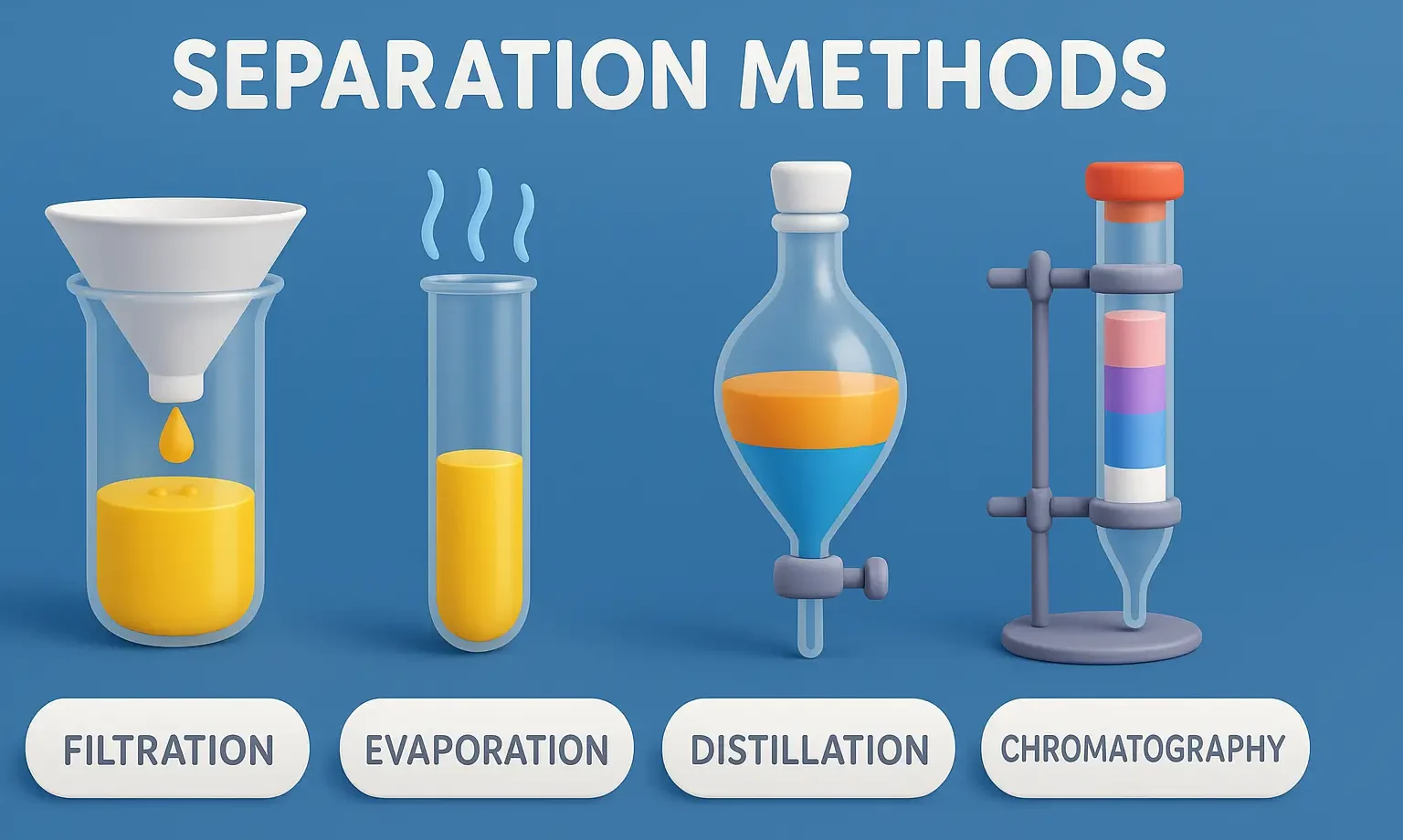
Separation Methods
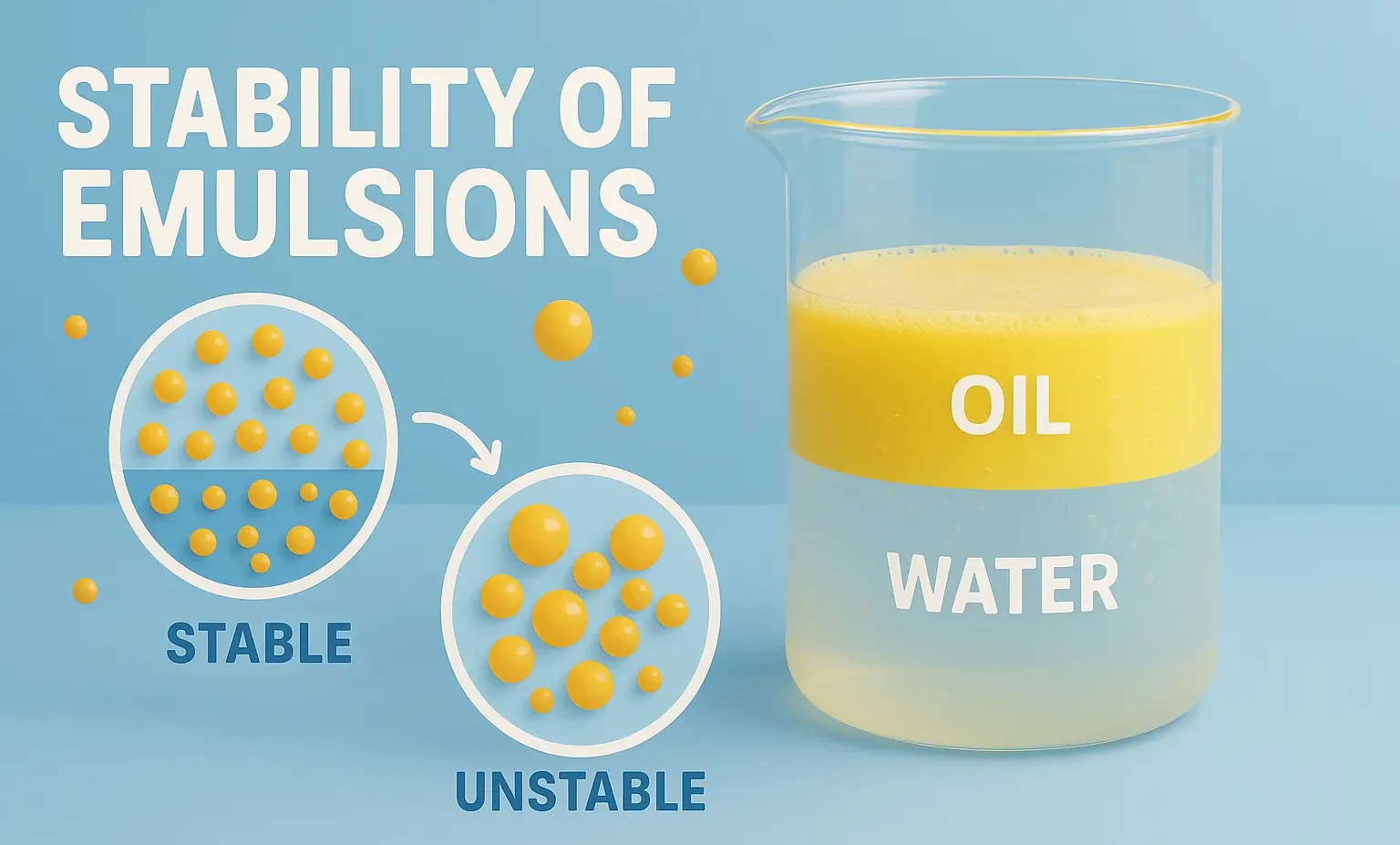
Separation Methods are vital in pharmaceuticals, chemistry, food, and environmental analysis. Separation Methods involve techniques to isolate and purify components from mixtures efficiently. These are based on the physical separation of particles by size, using external forces. Sieving Applicable to coarse particles (>50 µm). A stack of sieves with decreasing mesh size is used. The … Read more