- Chlorpromazine Hydrochloride blocks dopamine receptors, offering sedative and antipsychotic properties.
- Chlorpromazine Hydrochloride treats schizophrenia, nausea, and anxiety through its antipsychotic effects.
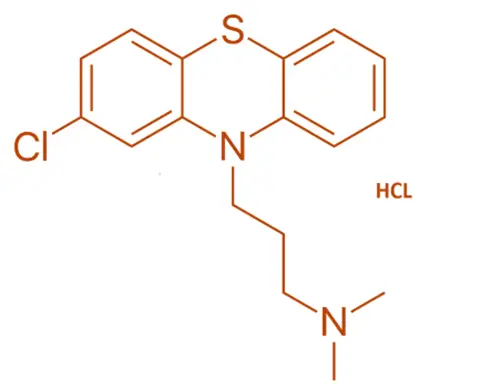
Chemical Formula:
- C₁₇H₁₉ClN₂S·HCl
Mechanism of Action:
- Strong D2 receptor blocker (limbic system, basal ganglia)
- Also blocks α1-adrenergic, muscarinic, and histamine H1 receptors
Therapeutic Uses:
- Schizophrenia
- Acute psychosis
- Severe agitation
- Intractable hiccups
- Nausea and vomiting
Side Effects:
- Sedation (H1 blockade)
- Hypotension (α1 blockade)
- Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS)
- Tardive dyskinesia
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
- Photosensitivity
- Cholestatic jaundice
SAR of Chlorpromazine and Phenothiazines
-
Phenothiazine ring system:
- Tricyclic core essential for antipsychotic activity.
-
Electron-withdrawing group at position 2 (e.g., Cl):
- Enhances potency by increasing affinity for D₂ receptors.
-
3-carbon linker chain:
- Optimal distance between the nitrogen and tricyclic ring for D₂ receptor antagonism.
-
Terminal amine:
- Tertiary amine is common; pKa influences CNS penetration.
- Substituents can affect potency and side effect profile (sedation, EPS).
-
Lipophilicity:
- Affects CNS penetration and onset.
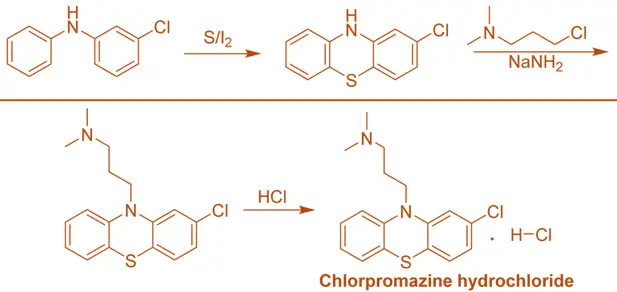
Synthesis of Chlorpromazine
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos