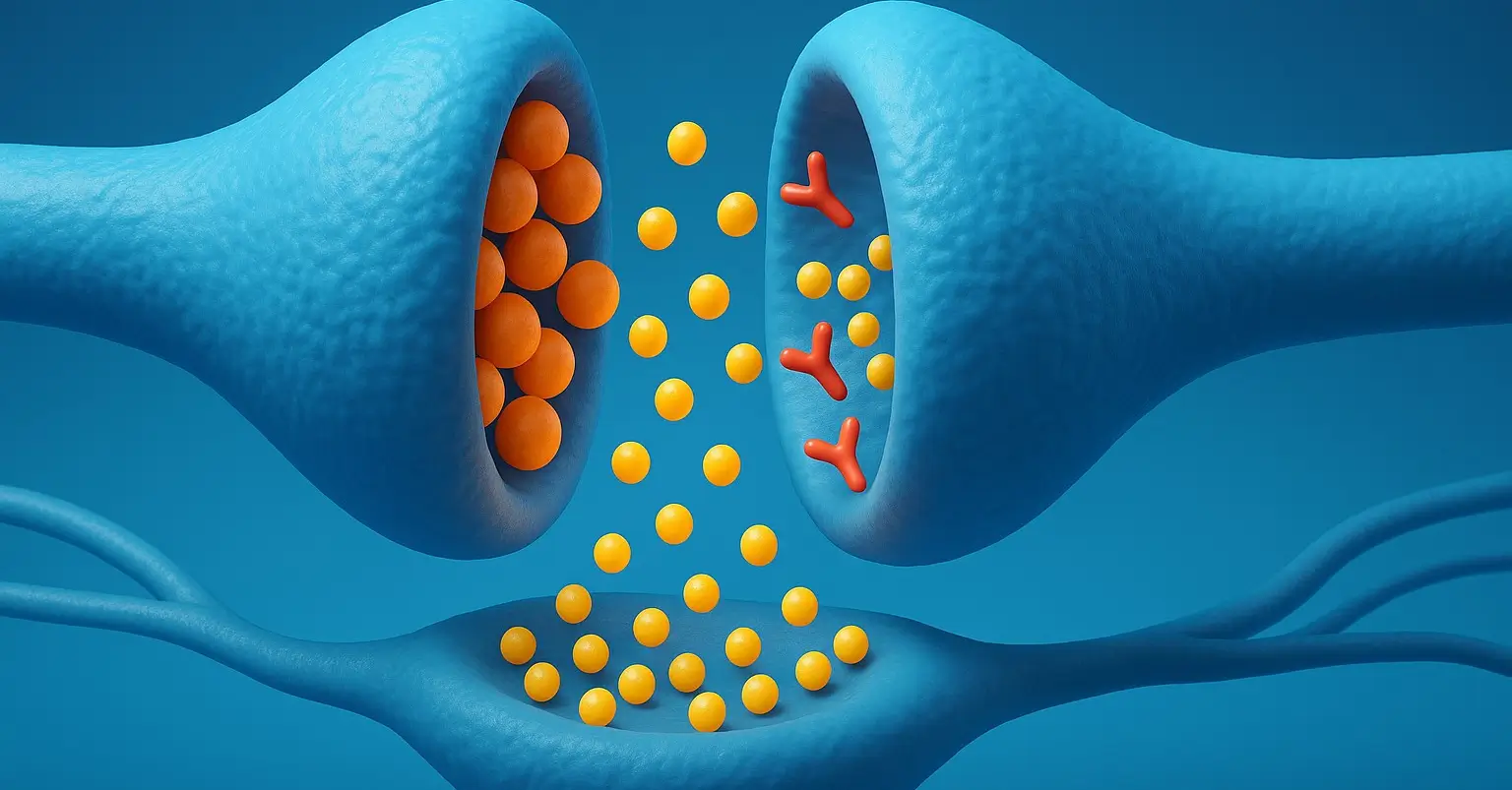
- Cholinergic neurotransmitters refer specifically to acetylcholine (ACh), a key chemical messenger used by certain neurons to communicate with each other or with muscle cells.
- These neurons are called cholinergic neurons because they release acetylcholine as their primary neurotransmitter.
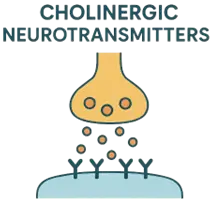
Function and Importance of Cholinergic Neurotransmitters
- Acetylcholine is involved in various physiological functions depending on where in the body it’s acting:
- In the Central Nervous System (CNS): It’s important for learning, memory, attention, and arousal.
- In the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
- In the somatic nervous system, it stimulates skeletal muscle contraction.
- In the autonomic nervous system, it:
- Acts on all preganglionic neurons (both sympathetic and parasympathetic).
- Acts on postganglionic parasympathetic neurons.
- In a few cases, it acts on postganglionic sympathetic neurons (like sweat glands).
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements