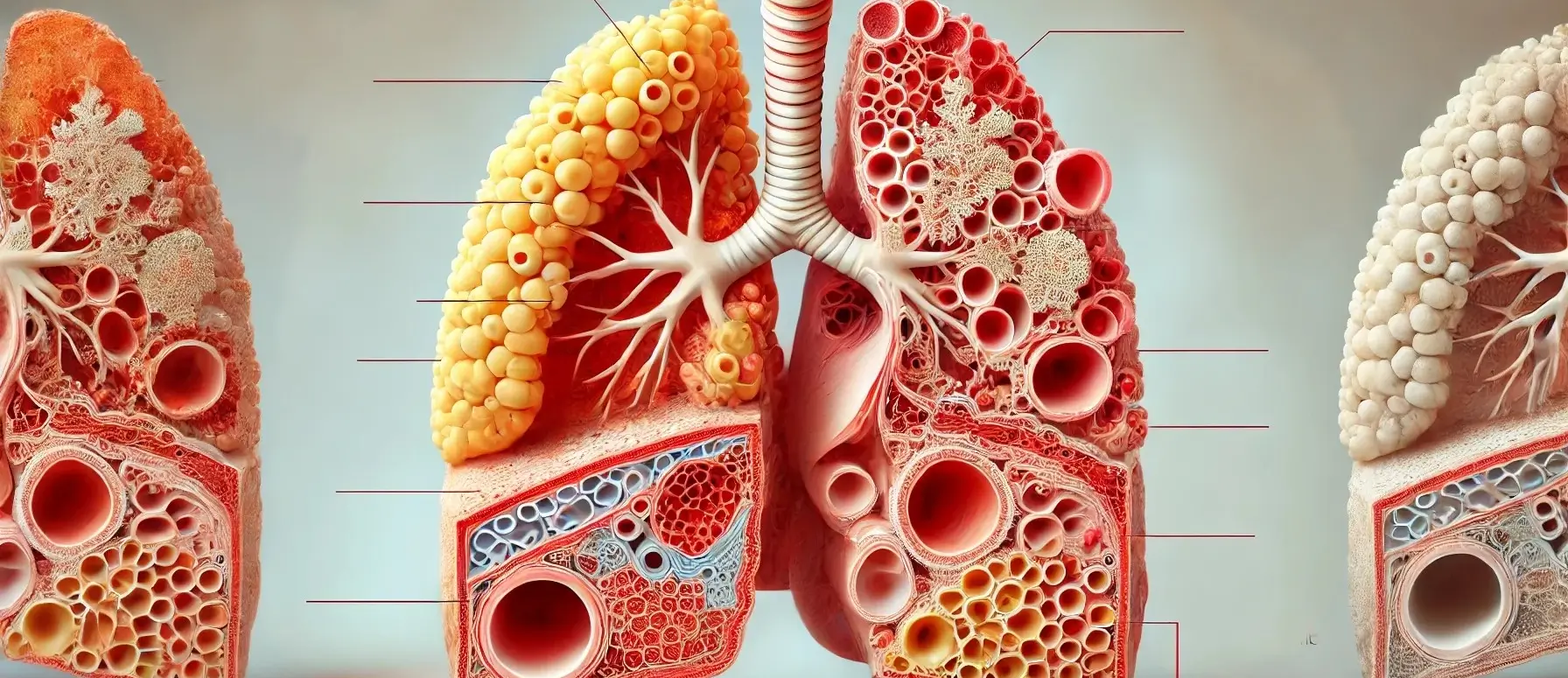
Chronic Obstructive Airway Diseases Introduction
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a group of progressive lung diseases characterized by persistent airflow limitation and increased inflammation in the airways.
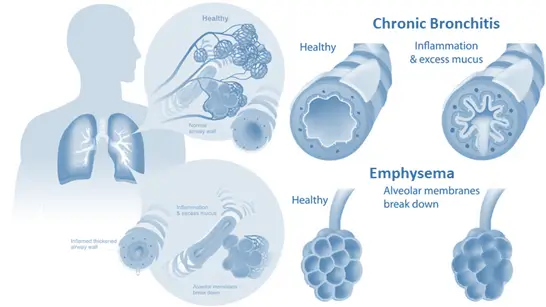
- It primarily includes two main conditions:
-
Chronic Bronchitis:
- Inflammation of the bronchi leading to increased mucus production and airway narrowing, resulting in a persistent cough often called a “smoker’s cough.”
-
Emphysema:
- Damage to the alveoli where gas exchange occurs.
- The alveolar walls break down and lose elasticity, leading to enlarged air spaces, impaired oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange, and reduced lung function.
Advertisements
- Chronic Obstructive Airway Diseases conditions often occur together, causing difficulty breathing, coughing, and increased mucus production.
- COPD is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, primarily caused by long-term exposure to lung irritants such as tobacco smoke, air pollution, and occupational dust or chemicals.
Pathophysiology of COPD
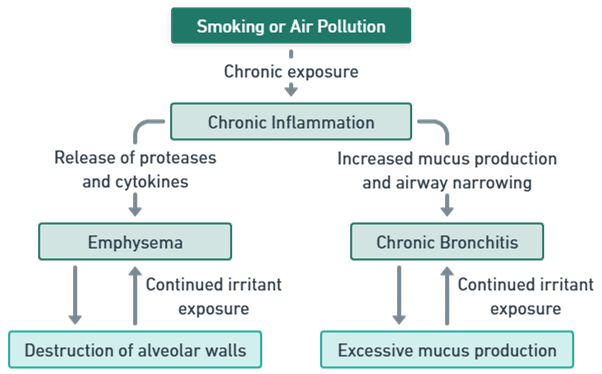
- The primary cause of COPD is long-term exposure to lung irritants, particularly tobacco smoke.
- These irritants trigger an inflammatory response in the airways, leading to the release of inflammatory cells and mediators that cause damage to lung tissue.
- Chronic Bronchitis: Inflammation results in increased mucus production and narrowing of the airways.
- Emphysema: Inflammation leads to the destruction of alveolar walls.
- The combination of airway inflammation, mucus production, and alveolar damage results in airflow limitation, making it difficult for air to move in and out of the lungs.
- This causes symptoms such as shortness of breath, wheezing, and chronic cough, as well as reduced lung function and exercise capacity.
Symptoms of COPD
- Common symptoms of COPD include:
- Persistent Cough: Often with mucus production.
- Shortness of Breath: Especially during physical activity.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound when breathing.
- Chest Tightness or Pain
- Fatigue: Reduced exercise capacity.
- Frequent Respiratory Infections
Diagnosis and Management of COPD
- COPD is typically diagnosed based on:
- Medical History: Assessment of symptoms and exposure to risk factors.
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs like wheezing and decreased breath sounds.
- Lung Function Tests:
- Spirometry: Measures the amount and speed of air inhaled and exhaled to assess airflow limitation.
Management and Treatment
- While there is no cure for COPD, management strategies aim to reduce symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression.
Advertisements
-
Smoking Cessation
- Most Critical Step: Quitting smoking prevents further lung damage and reduces complications.
-
Medications
- Bronchodilators: Relax airway muscles to improve airflow.
- Short-Acting (e.g., albuterol)
- Long-Acting (e.g., salmeterol)
- Inhaled Corticosteroids: Reduce airway inflammation (e.g., beclomethasone, budesonide).
- Combination Inhalers: Contain both a bronchodilator and a corticosteroid.
- Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors: Reduce inflammation and relax airways (e.g., roflumilast).
- Antibiotics: Treat bacterial infections that can worsen symptoms.
- Bronchodilators: Relax airway muscles to improve airflow.
-
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
- A comprehensive program including exercise training, nutritional advice, and education to help manage symptoms and improve physical conditioning.
-
Oxygen Therapy
- For patients with severe COPD and low blood oxygen levels to improve oxygenation.
-
Surgical Interventions
- Lung Volume Reduction Surgery: Removes diseased lung tissue to enhance breathing efficiency.
- Lung Transplantation: Considered in severe cases where other treatments have failed.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Healthy Diet: Balanced nutrition to support overall health.
- Regular Exercise: Improves cardiovascular fitness and muscle strength.
- Avoiding Lung Irritants: Minimize exposure to pollutants, dust, and chemical fumes.
- Vaccinations: Regular flu and pneumococcal vaccines to prevent infections that can exacerbate COPD.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements