Discover how Cimetidine works as an H2 blocker to reduce stomach acid and treat ulcers GERD and related digestive disorders.
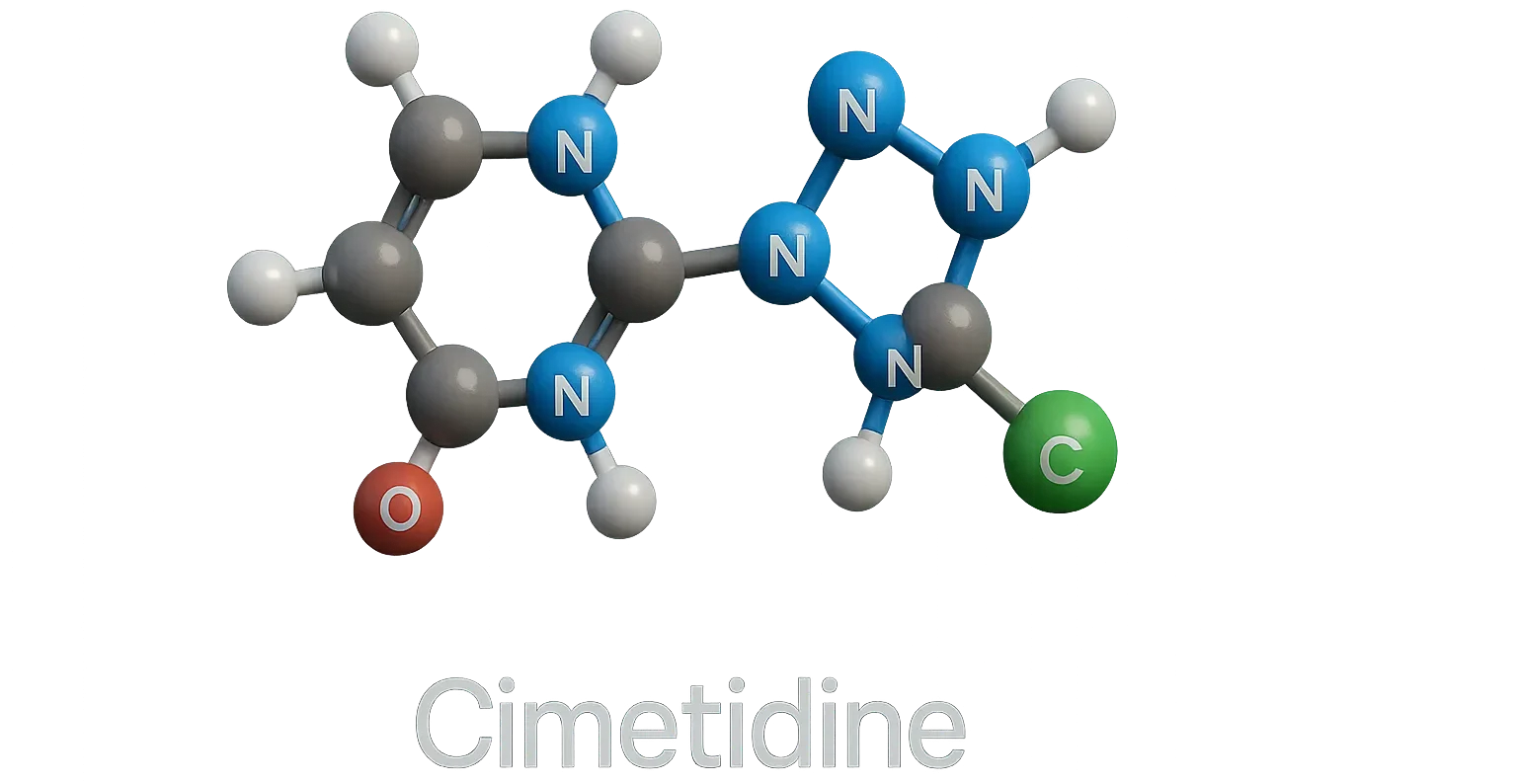
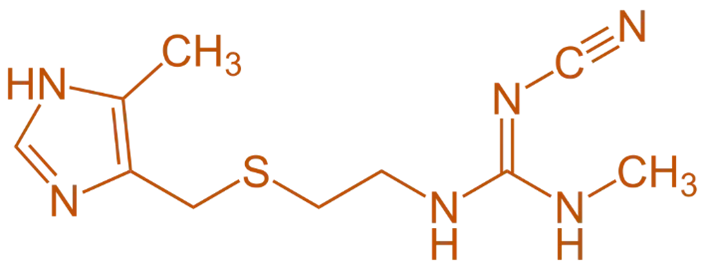
Structure of Cimetidine
- It is a first-generation H₂-receptor antagonist featuring a thiazole ring connected to a dimethylamine side chain and an imidazole moiety.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₆H₂₄N₄S
Mode of Action
- Cimetidine selectively inhibits H₂ receptors on parietal cells in the stomach, reducing the secretion of gastric acid.
- It competitively blocks histamine from binding to these receptors, thereby decreasing acid production.
Uses
- Peptic Ulcers: Promotes healing by reducing stomach acid.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Alleviates symptoms by lowering acid levels.
- Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome: Manages excessive gastric acid secretion.
- Prevention of Stress Ulcers: Used in critically ill patients to prevent ulcer formation.
Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
- Thiazole Ring: Essential for binding affinity to H₂ receptors.
- Imidazole Moiety: Enhances receptor selectivity and inhibitory potency.
- Dimethylamine Side Chain: Increases solubility and facilitates interaction with the receptor.
- Substituents: Methyl groups on the thiazole ring improve metabolic stability and binding strength.
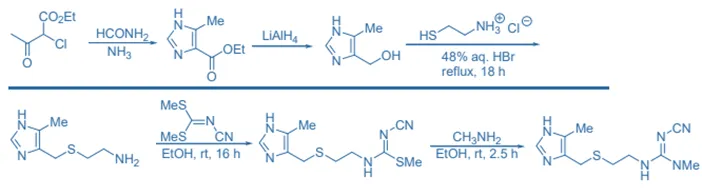
Synthesis of Cimetidine