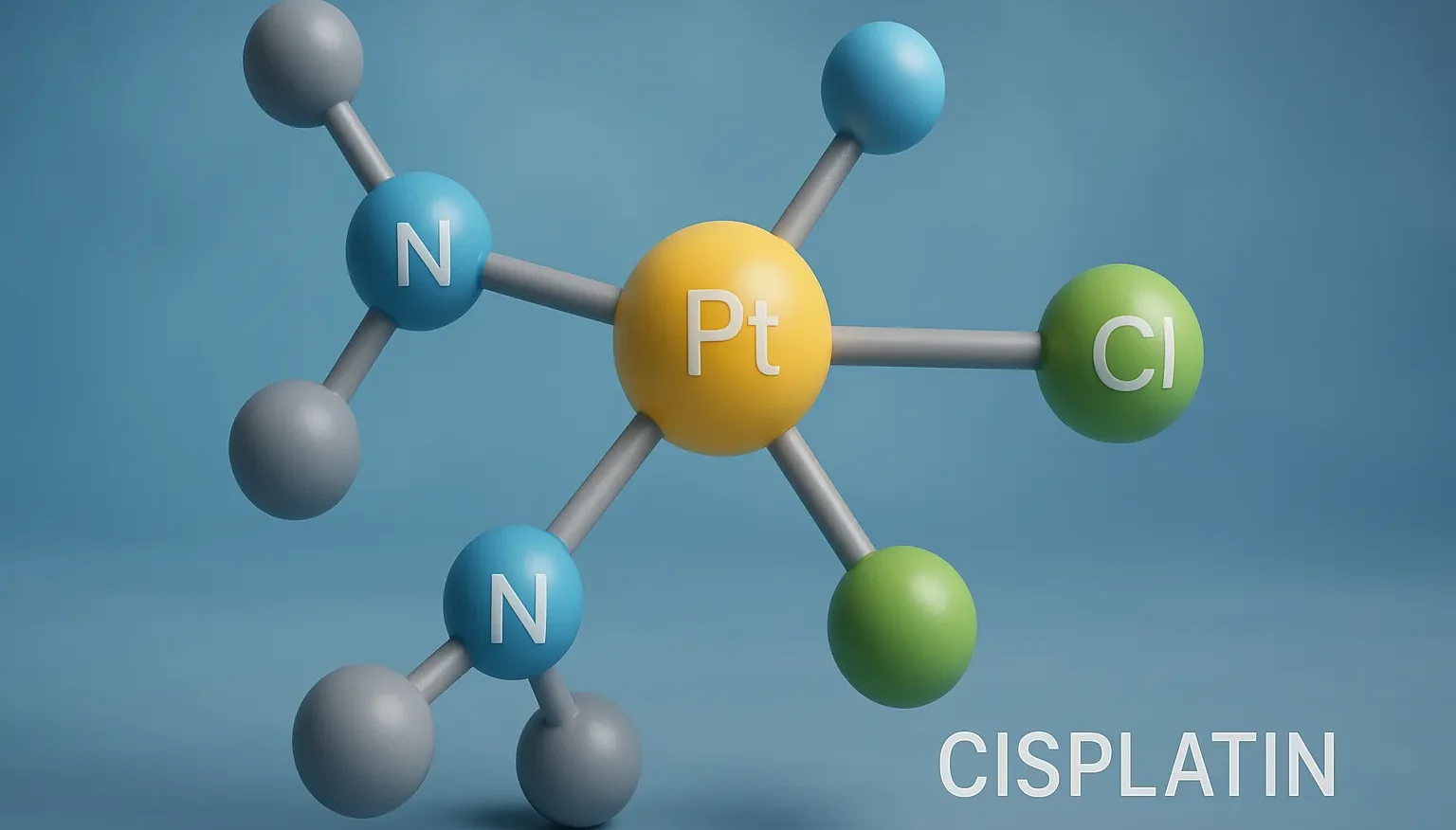
Cisplatin is an anti-neoplastic agent used in various cancers by forming DNA crosslinks, which inhibit replication and trigger cell death.
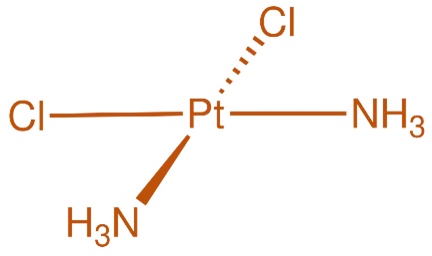
Structure of Cisplatin
- Cisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapeutic agent with a square planar geometry, featuring two chloride ligands and two amine groups bound to a central platinum atom.
- Chemical Formula: C₆H₁₈Cl₂N₄Pt
Mode of Action
- DNA Crosslinking: Forms intrastrand and interstrand crosslinks in DNA, disrupting DNA replication and transcription.
- DNA Repair Inhibition: Prevents cancer cells from repairing DNA damage.
- Apoptosis Induction: Leads to programmed cell death in malignant cells.
Advertisements
Uses
- Testicular Cancer: Highly effective, often leading to cures.
- Ovarian Cancer: As part of combination chemotherapy regimens.
- Bladder Cancer: In combination with other chemotherapeutic agents.
- Lung Cancer: Particularly non-small cell lung carcinoma.
- Head and Neck Cancers: As part of multi-agent chemotherapy.