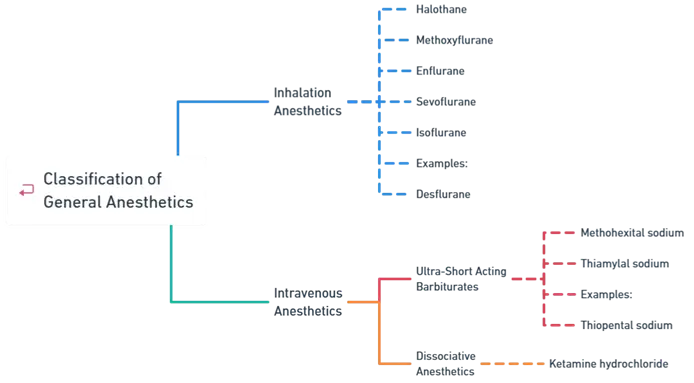
- Classification of General Anesthetics is based on route (inhalation, intravenous) and chemical nature.
- General anesthetics are classified based on:
- Route of Administration
- Chemical Structure
-
Inhalation Anesthetics
- These are gases or volatile liquids administered via inhalation.
- Common for their ease of control and pleasant induction.
- Examples:
-
Intravenous Anesthetics
- Administered through the bloodstream.
- Commonly used for induction, followed by maintenance with inhalation agents.
-
Ultra-Short Acting Barbiturates
- Rapidly act on the central nervous system to induce unconsciousness.
- Examples:
-
Dissociative Anesthetics
- Induce analgesia and amnesia without full loss of consciousness.
- Example:
General Anesthetics Classification Table
| Class | Mode of Action | Uses | Common Side Effects | Examples |
| Inhalation Anesthetics | Enhance GABA-A receptor activity, inhibit NMDA receptors (varies by drug), causing CNS depression | Induction and maintenance of general anesthesia | Hypotension, respiratory depression, nausea, hepatotoxicity | Halothane*, Methoxyflurane, Enflurane, Sevoflurane, Isoflurane, Desflurane |
| Ultra-short Acting Barbiturates | Potentiate GABA-A receptor activity, leading to CNS depression | Induction of anesthesia, short procedures | Respiratory depression, hypotension, hangover effect | Methohexital sodium*, Thiamylal sodium, Thiopental sodium |
| Dissociative Anesthetics | NMDA receptor antagonist; causes functional dissociation between cortical and limbic systems | Induction of anesthesia, minor procedures, especially in children | Hallucinations, increased intracranial pressure, hypertension, emergence delirium | Ketamine hydrochloride* |
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos