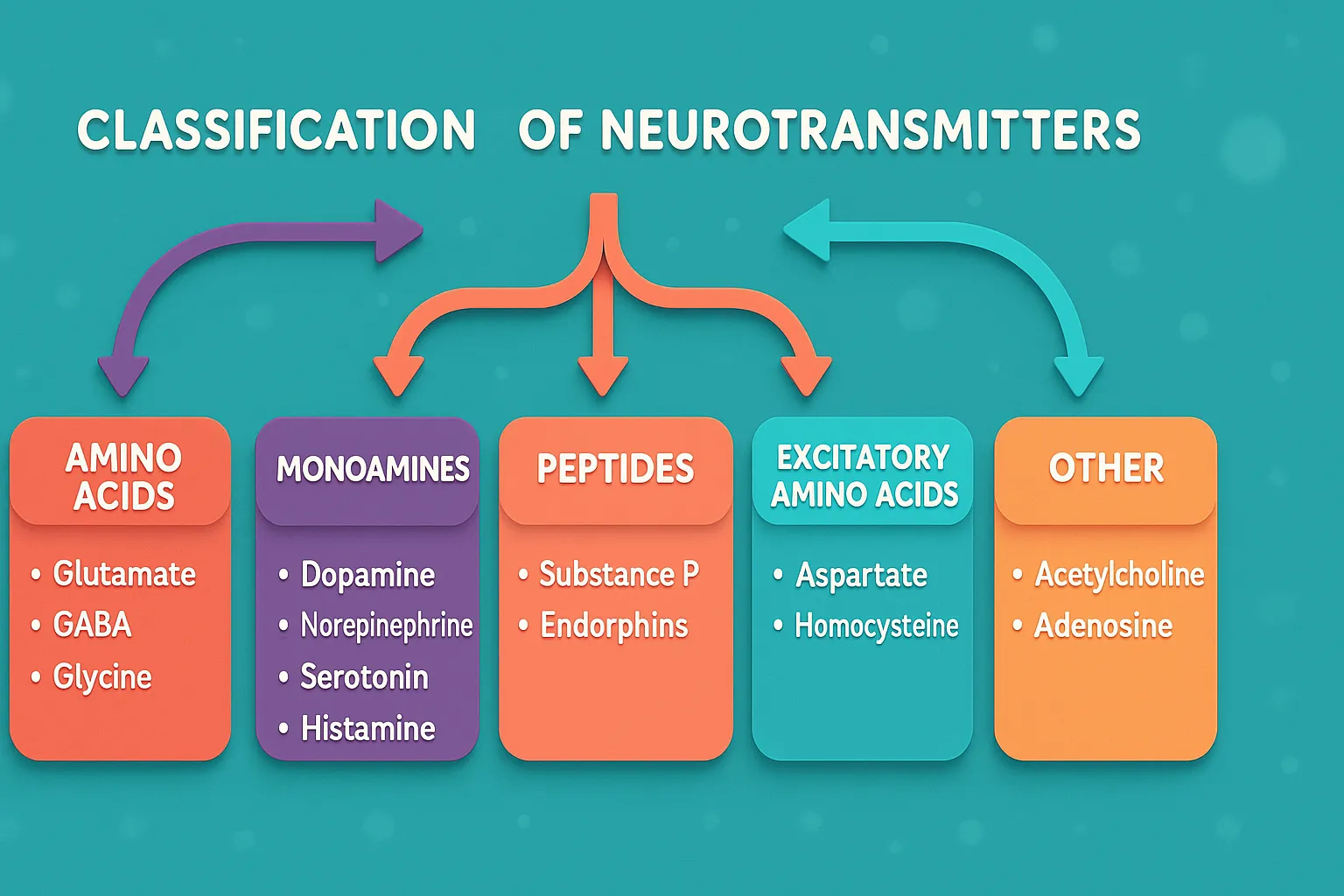
Neurotransmitters are classified as excitatory, inhibitory, or modulatory, based on their role in nerve signaling.
-
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
- These promote depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane, increasing the likelihood of an action potential.
- Glutamate: Main excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS
- Aspartate: Excitatory amino acid in the CNS
- Acetylcholine: Excitatory at the neuromuscular junction (nicotinic receptors)
- Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline): Excitatory in the sympathetic nervous system and CNS
- Epinephrine (Adrenaline): Excitatory in various CNS and peripheral pathways
- Histamine: Excitatory in the brain; involved in arousal and wakefulness
- These promote depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane, increasing the likelihood of an action potential.
-
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
- These cause hyperpolarization, making it less likely for the postsynaptic neuron to fire.
- GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid): Primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS
- Glycine: Inhibitory, especially in the spinal cord
- Serotonin (5-HT): Often inhibitory; effects vary by receptor subtype
- These cause hyperpolarization, making it less likely for the postsynaptic neuron to fire.
-
Neurotransmitters with Both Excitatory and Inhibitory Actions
- These can act as either excitatory or inhibitory depending on the receptor subtype and location.
- Dopamine: Can be excitatory (D1 receptors) or inhibitory (D2 receptors)
- Acetylcholine: Excitatory at neuromuscular junctions; inhibitory in some CNS regions (muscarinic receptors)
- Serotonin (5-HT): Effects depend on receptor subtype (can be both)
- Nitric Oxide: Gaseous neurotransmitter with variable modulatory effects
- These can act as either excitatory or inhibitory depending on the receptor subtype and location.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos