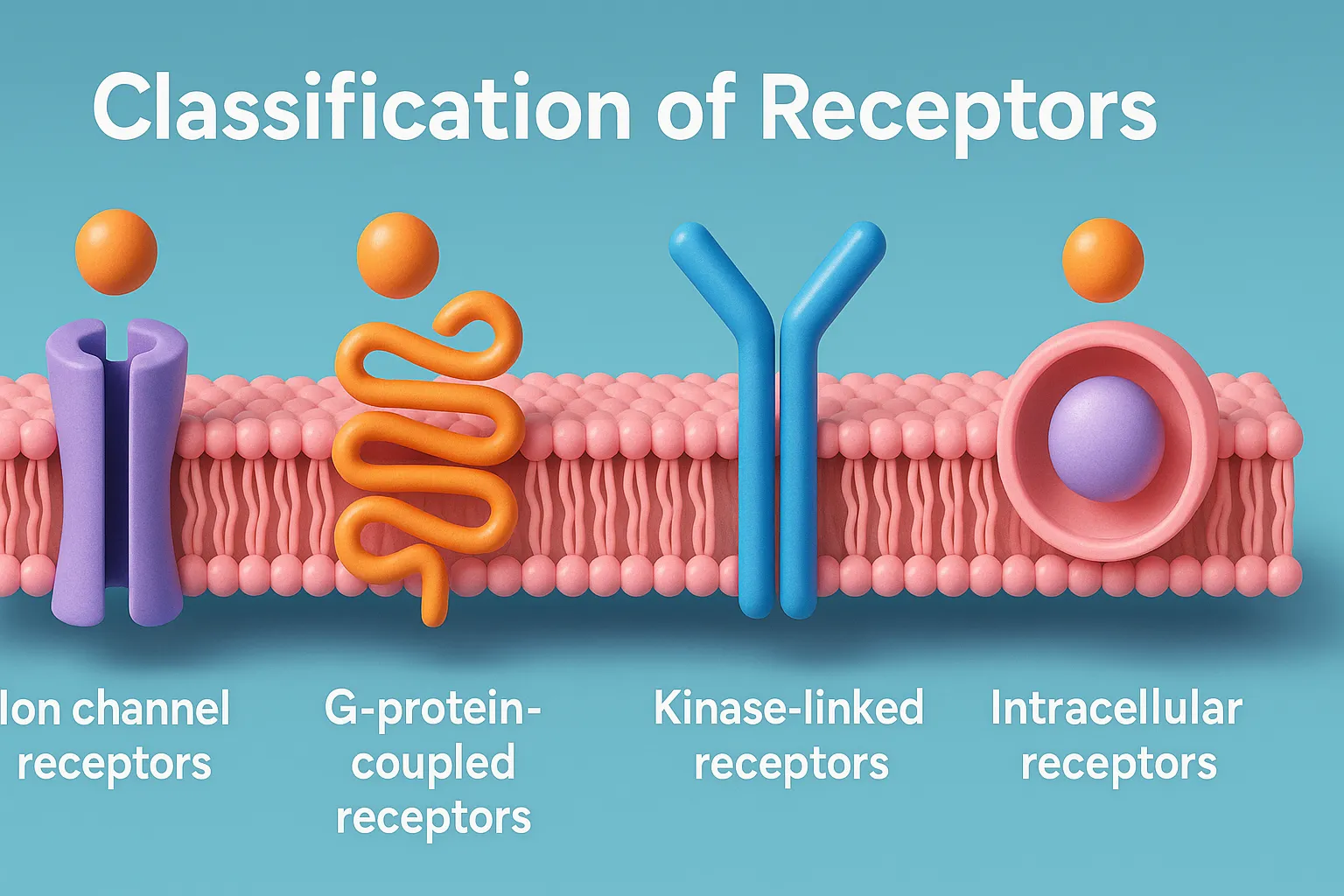
Classification of receptors is based on structure, function, and response, including ion channel, GPCR, enzyme, and nuclear types.
Classification of Receptors
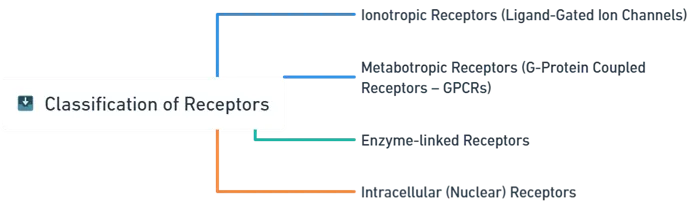
Receptors are classified based on their structure and signal transduction mechanism:
-
Ionotropic Receptors (Ligand-Gated Ion Channels)
- Response in milliseconds.
- Example: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, GABA-A receptor.
-
Metabotropic Receptors (G-Protein Coupled Receptors – GPCRs)
- Response in seconds.
- Involves G-proteins and second messengers (like cAMP, IP3).
- Example: β-adrenergic receptors, muscarinic receptors.
-
Enzyme-linked Receptors
- Have intrinsic enzymatic activity (often tyrosine kinase).
- Response in minutes to hours.
- Example: Insulin receptor, EGF receptor.
-
Intracellular (Nuclear) Receptors
- Located in cytoplasm or nucleus.
- Bind lipid-soluble drugs (like steroids), altering gene transcription.
- Response in hours to days.
- Example: Glucocorticoid receptor, thyroid hormone receptor.