- The classification of tablets includes oral, buccal, sublingual, vaginal, and implantable tablets, each designed for specific delivery sites.
- The classification of tablets also includes immediate release, sustained release, delayed release, and controlled release forms.
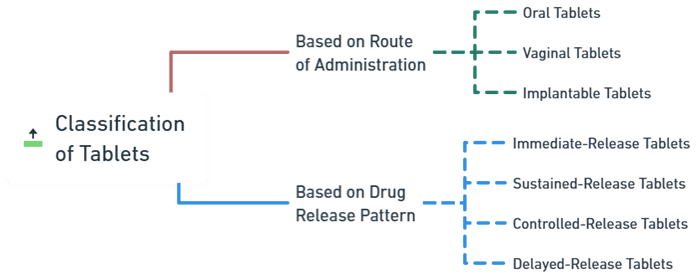
Based on Route of Administration:
-
Oral Tablets:
- Conventional Tablets: Disintegrate and dissolve in the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., Paracetamol).
- Chewable Tablets: Meant to be chewed before swallowing (e.g., Antacids).
- Effervescent Tablets: Dissolve in water before administration (e.g., Vitamin C).
- Sublingual Tablets: Dissolve under the tongue for rapid absorption (e.g., Nitroglycerin).
- Buccal Tablets: Dissolve in the buccal pouch for slow absorption (e.g., Fentanyl).
-
Vaginal Tablets:
- Inserted into the vagina for localized treatment (e.g., Clotrimazole).
-
Implantable Tablets:
- Placed under the skin for long-term drug release (e.g., Hormonal implants).
Classification of Tablets Based on Drug Release Pattern:
- Immediate-Release Tablets: Quickly disintegrate and release the drug.
- Sustained-Release Tablets: Gradual release over time.
- Controlled-Release Tablets: Precisely control the drug release rate.
- Delayed-Release Tablets: Release drugs at a specific site in the GIT (e.g., Enteric-coated tablets).
Advertisements

