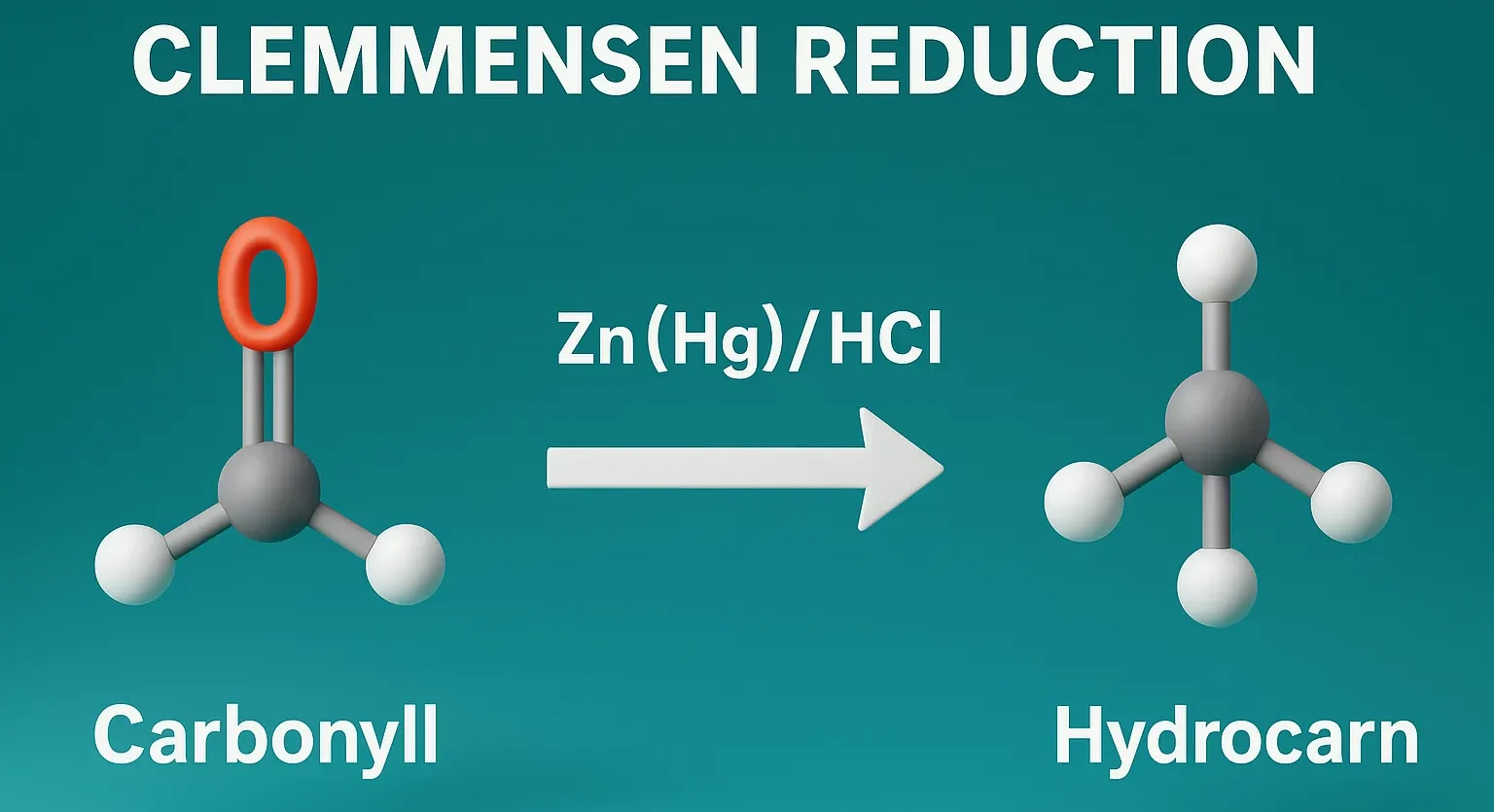
- Clemmensen Reduction transforms carbonyl compounds into hydrocarbons using Zn–Hg and HCl in organic synthesis.
- Type: Metal-acid reduction
Purpose of Clemmensen Reduction:
- Reduces aldehydes and ketones to alkanes.
- Used especially for carbonyl groups adjacent to aromatic rings (aryl ketones).
Advertisements
Reagents of Clemmensen Reduction:
- Zinc amalgam (Zn(Hg))
- Concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Reaction is acidic
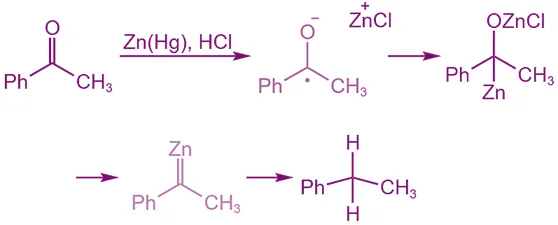
Mechanism (Simplified Concept):
-
Coordination to Zinc:
- The carbonyl oxygen coordinates to the Zn surface, making the C=O bond more electrophilic.
-
Single Electron Transfer (SET):
- Zn donates an electron to the carbonyl carbon → forms radical anion.
-
Protonation:
- Proton from acid (HCl) stabilizes the intermediate.
-
Further Reduction and Protonation:
- Repeated electron transfer and protonation convert the C=O group to -CH₂-.

- Best used for aromatic ketones where acid-sensitive groups are absent.
- Repeated electron transfer and protonation convert the C=O group to -CH₂-.
Advertisements
Advertisements
Conditions:
- Harshly acidic, so acid-sensitive compounds may degrade.
Example:
-
- Ar-CO-R + Zn(Hg)/HCl → Ar-CH₂-R
- Benzophenone → Diphenylmethane
Advertisements