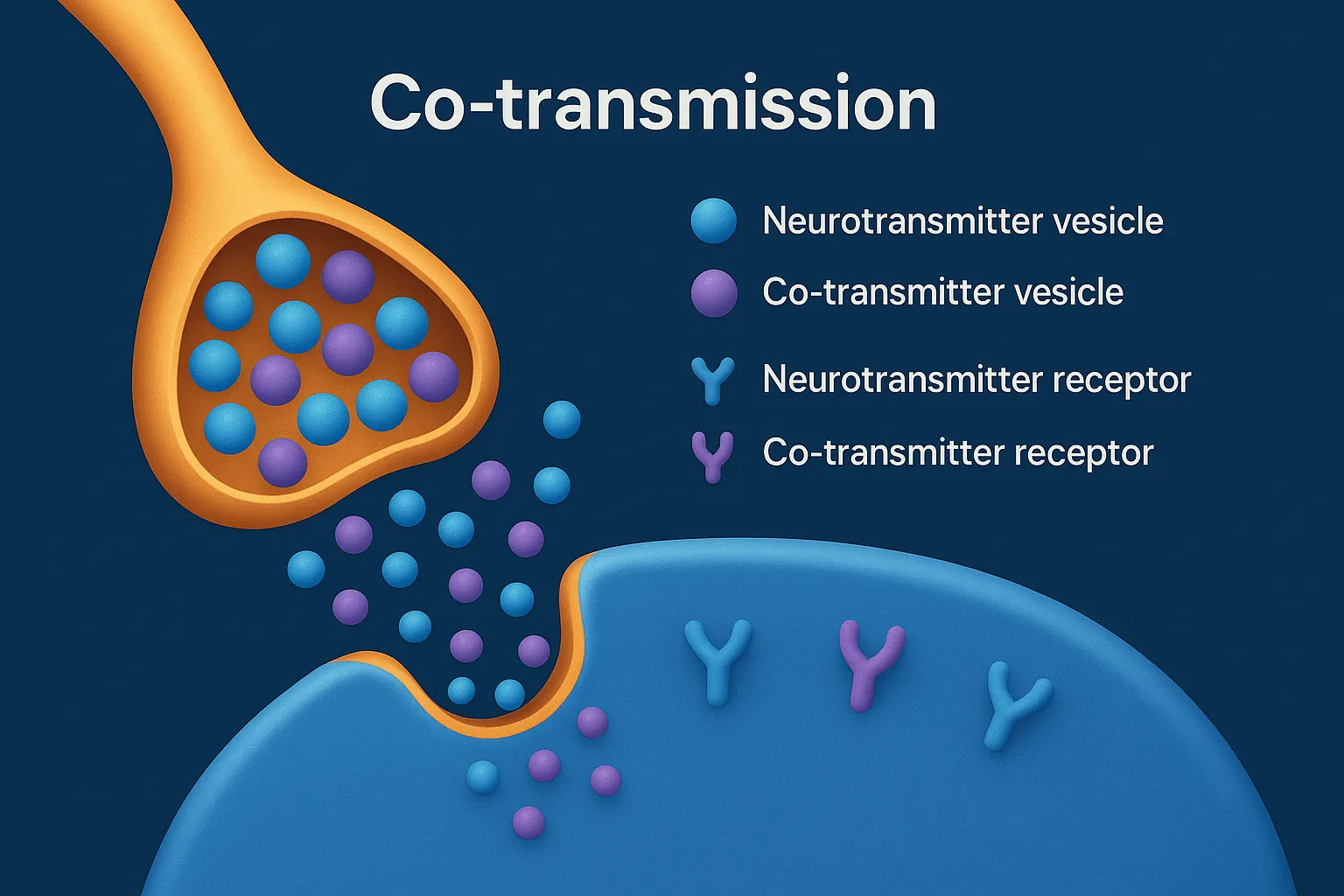
Co-transmission occurs when neurons release multiple neurotransmitters to regulate complex physiological responses.
Definition of Co-transmission:
- It is the simultaneous release of more than one neurotransmitter from a single neuron, usually from the same synaptic vesicle or nearby vesicles.
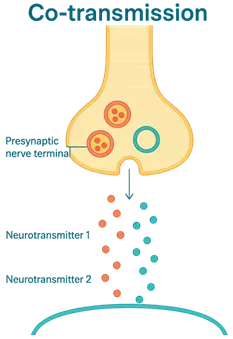
Key Features:
- Neurotransmitters can be classical (e.g., acetylcholine) and peptides (e.g., substance P) or amines (e.g., dopamine).
- These co-transmitters can:
- Act on different receptors
- Produce short- and long-term effects
- Modify the action of the main transmitter (synergistic or modulatory)
Examples:
- Noradrenaline + ATP + Neuropeptide Y (released from sympathetic nerves)
- Acetylcholine + VIP (vasoactive intestinal peptide) (in parasympathetic nerves)
- Dopamine + Substance P (in certain brain regions)