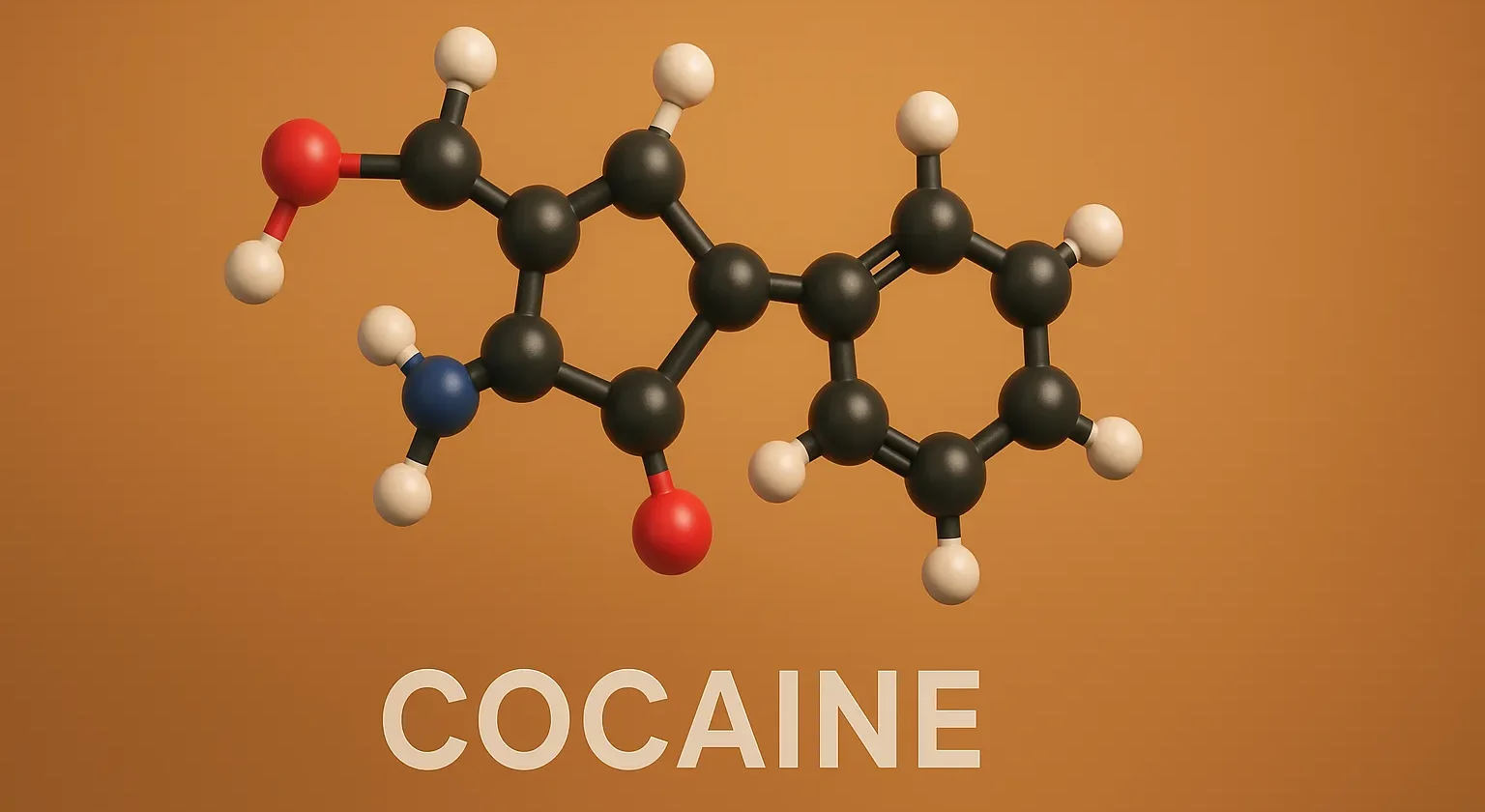
Cocaine is a natural ester local anesthetic that blocks nerve conduction and is also known for its stimulant and addictive properties.
Structure of Cocaine
- It is a naturally occurring local anesthetic derived from the coca plant, featuring a tropane ring system with a benzoyl and methyl ester substituent.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₇H₂₃NO₄

Mode of Action
- Sodium Channel Blockade: Inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels, preventing nerve impulse conduction.
- Vasoconstriction: Causes local vasoconstriction by stimulating alpha-adrenergic receptors.
- Sympathomimetic Effects: Increases heart rate and blood pressure due to central nervous system stimulation.
Uses
- Local Anesthesia: Used in nasal surgery, ear surgery, and ophthalmic procedures.
- Topical Preparations: Employed in topical creams and sprays for numbing mucous membranes.
- Addiction Treatment: Limited use in treating cocaine dependence under medical supervision.
Side Effects of Cocaine
- Cardiovascular Toxicity: Arrhythmias, hypertension, and tachycardia.
- Central Nervous System Stimulation: Anxiety, seizures, and agitation.
- Local Tissue Irritation: Can cause mucosal damage and necrosis with prolonged use.