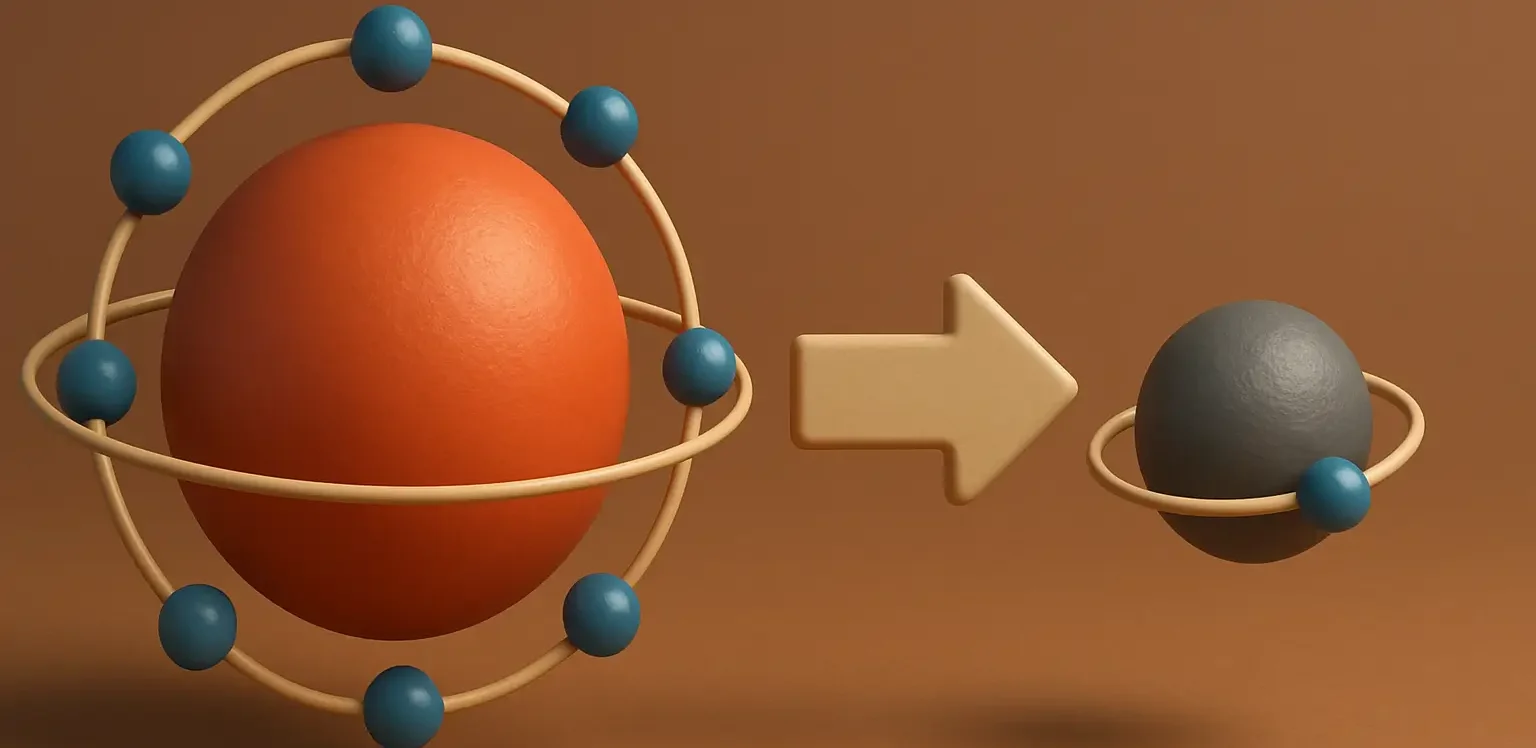
- Concept of Oxidation is a process in which a chemical species loses one or more electrons, leading to an increase in its oxidation state.
- In simpler terms, the species becomes more positively charged.
- Oxidation is often associated with the addition of oxygen to a substance or the removal of hydrogen from it.
- However, the key factor that defines oxidation is the loss of electrons.
Example of Concept of Oxidation:
- Consider the reaction between magnesium metal (Mg) and oxygen gas (O₂) to form magnesium oxide (MgO).
- Mg (s) + 12O₂ (g) → MgO (s)
- In this reaction, magnesium loses two electrons to become the Mg²⁺ ion, as shown below:
- Mg (s) → Mg²⁺ (s) + 2e−
- Magnesium has been oxidized, as it has lost electrons, and its oxidation state has increased from 0 to +2.
Oxidizing Agents
- An oxidizing agent is a substance that gains electrons in a redox reaction, causing the oxidation of another species.
- By accepting electrons from another species, it enables that species to lose electrons, leading to its oxidation.
- As a result, the oxidizing agent itself gets reduced in the process. Oxidizing agents typically have a high affinity for electrons and can be identified by their ability to oxidize other substances.
-
Example:
- In the reaction between hydrogen gas (H₂) and oxygen gas (O₂) to form water (H₂O):
- 2H₂ (g) + O₂ (g) → 2H₂O (l)
- Oxygen (O₂) is the oxidizing agent, as it gains electrons from hydrogen (H₂) during the reaction, leading to the reduction of oxygen and the oxidation of hydrogen.
- In the reaction between hydrogen gas (H₂) and oxygen gas (O₂) to form water (H₂O):
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements