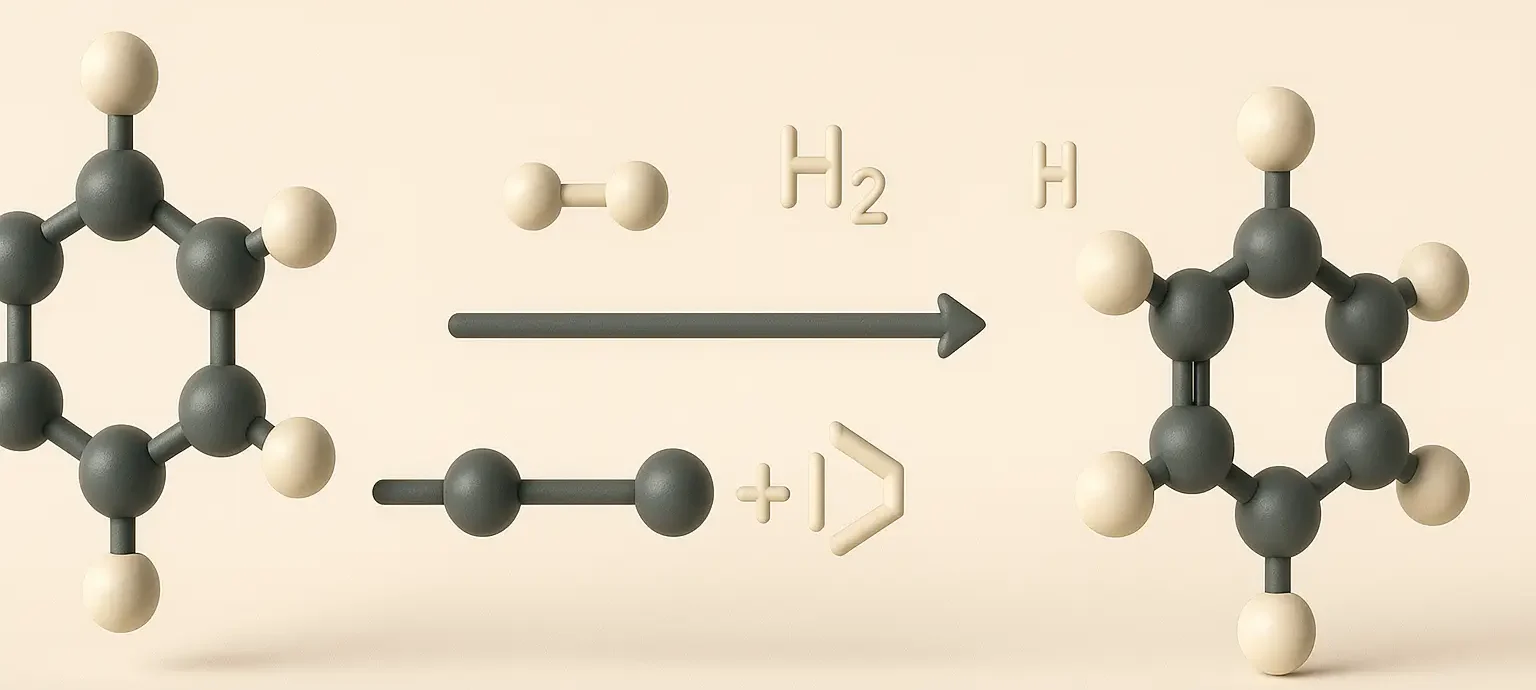Cycloalkanes Methods of Preparation
Generally, there are four Cycloalkanes Methods of Preparation which are stated below with the examples:
1. Hydrogenation of Aromatic Compounds:
-
- Process: Aromatic compounds like benzene can be hydrogenated in the presence of a catalyst (usually nickel, palladium, or platinum) under high pressure to produce cycloalkanes.
- Example: C6H6 (benzene) + 3H2 → Ni, heat (Reagents)→ C6H12 (cyclohexane)
2. Wurtz Reaction:
-
- Process: Haloalkanes undergo coupling reactions in the presence of sodium metal to form cycloalkanes. This method is particularly useful for synthesizing small and medium-sized rings.
- Example: 2CH2Cl-CH2Cl + 4Na → Cyclobutane + 4NaCl
3. Dieckmann Condensation (Intramolecular Claisen Condensation):
-
- Process: Dicarboxylic acids or their esters undergo intramolecular condensation to form cyclic ketones, which can be subsequently reduced to cycloalkanes.
- Example: Diethyl adipate → NaOEt (Reagents)→ Cyclopentanone → H2,Pd/C (Reagents) → Cyclopentane
4. Reduction of Cycloalkanones:
-
- Process: Cycloalkanones can be reduced using zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid (Clemmensen reduction) or hydrazine in basic conditions (Wolff-Kishner reduction) to yield cycloalkanes.
- Example: Cyclohexanone → Zn/Hg, HCl (reagents) → Cyclohexane
Important Chemical Reactions of Cycloalkanes
1. Halogenation:
-
- Process: Cycloalkanes react with halogens (e.g., Cl₂, Br₂) under UV light, leading to the formation of halo-cycloalkanes via a free radical mechanism.
- Example: C6H12 + Cl2 → hv → C6H11Cl + HCl
2. Combustion:
-
- Process: Like other hydrocarbons, cycloalkanes combust in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy.
- Example: C5H10 + 7.5O2 → 5CO2 + 5H2O
3. Cracking:
4. Ring-Opening Reactions:
-
-
- Process: Cycloalkanes, particularly smaller rings like cyclopropane and cyclobutane, can undergo ring-opening reactions due to their ring strain.
- Example: Cyclopropane + HBr → CH3CH2CH2Br
- (Ring-opening of cyclopropane with HBr to form 1-bromopropane)
-
5. Oxidation:
-
-
- Process: Cycloalkanes can be oxidized using strong oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate (KMnO₄) to form diols or ketones.
- Example: Cyclohexane → KMnO4 Cyclohexanone
- These methods and reactions are fundamental in organic synthesis and industrial chemistry, highlighting the versatility and importance of cycloalkanes in various applications.
-