Cyclothiazide is a thiazide diuretic used to manage hypertension and fluid retention by increasing renal excretion of sodium and water.
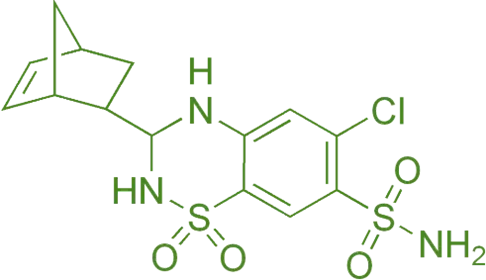
Structure of Cyclothiazide
- Cyclothiazide is a thiazide diuretic with a cyclohexane ring substitution, differing structurally from other thiazides.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₂H₁₅ClN₃O₄S₂
Mode of Action
- Thiazide Receptor Blocking: Inhibits the sodium-chloride symporter in the distal convoluted tubule.
- Sodium and Chloride Excretion: Promotes diuresis by increasing the excretion of sodium and chloride ions.
- Potassium Loss: Enhances excretion of potassium and hydrogen ions, potentially causing hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis.
Uses
- Hypertension: Utilized to reduce blood pressure through diuretic and vasodilatory effects.
- Edema: Treats fluid retention in conditions such as congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and renal disorders.
- Nephrolithiasis Prevention: Assists in preventing calcium-containing kidney stones.
- Heart Failure: Part of diuretic therapy to manage edema and reduce cardiac workload.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos