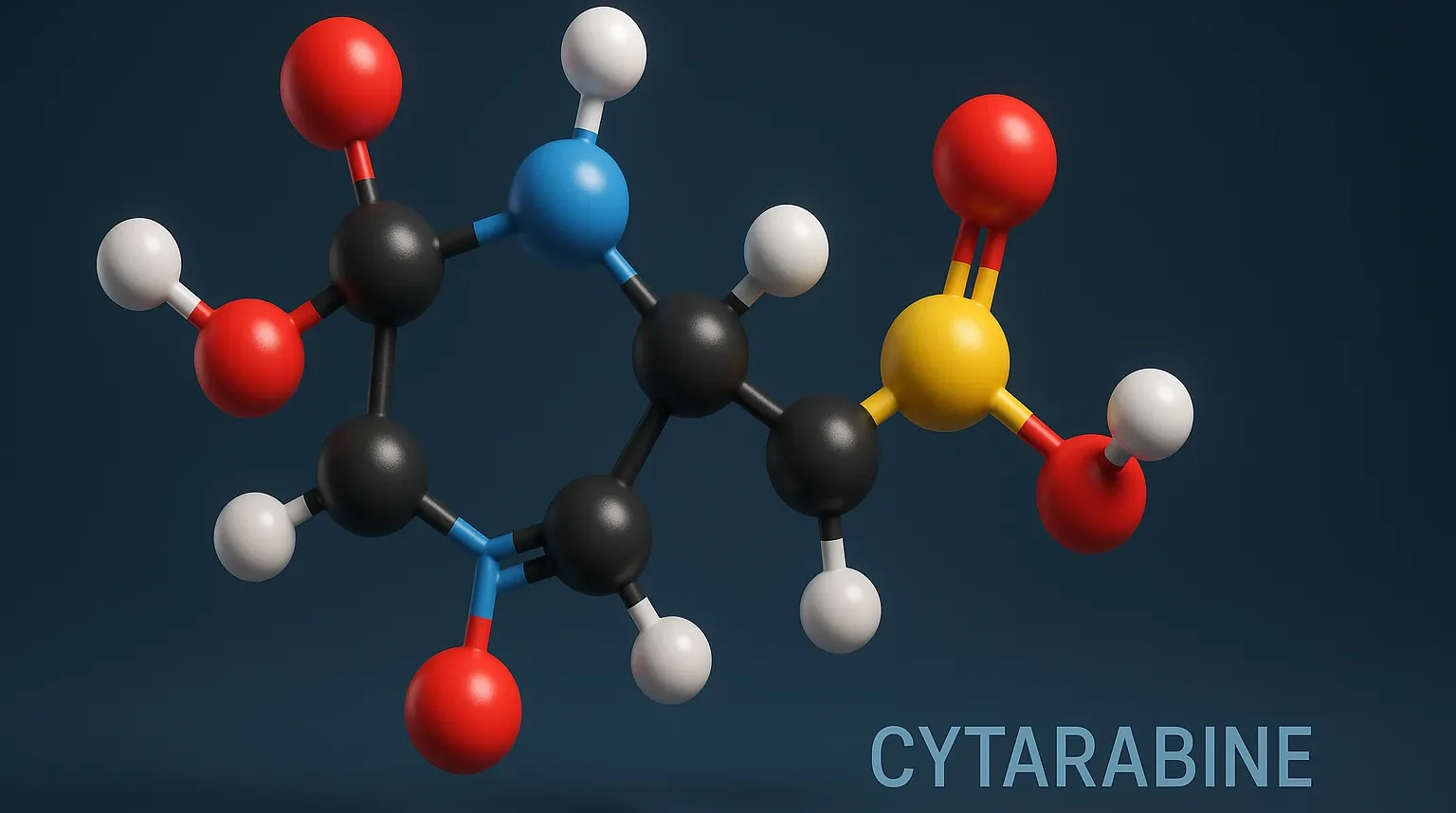
Cytarabine is an anti-neoplastic antimetabolite used in leukemia treatment by inhibiting DNA synthesis in rapidly dividing cancer cells.
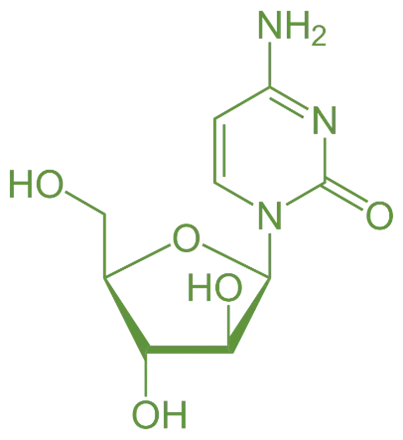
Structure of Cytarabine
- It is also known as Ara-C, is a pyrimidine analog with the following structural features:
- Cytosine Base: Similar to the natural nucleobase cytosine.
- Ribose Sugar: Modified with an arabinose moiety.
- Chemical Formula: C₄H₇N₃O₅
Mode of Action
- Cytarabine functions as an antimetabolite by:
- Inhibition of DNA Polymerase: Incorporates into DNA, causing chain termination.
- Inhibition of DNA Synthesis: Disrupts DNA replication and repair.
- Induction of Apoptosis: Causes cytotoxicity in rapidly dividing cells, particularly in leukemic cells.
Advertisements
Uses
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): As a cornerstone of induction and consolidation therapy.
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): In combination with other chemotherapeutic agents.
- Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: As part of multi-agent chemotherapy regimens.
- Hairy Cell Leukemia: In combination with other treatments.