- Designing an aseptic area involves creating a highly controlled environment to prevent contamination in processes such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, healthcare, or lab work.
Key Considerations in Designing of aseptic area
-
Regulatory Compliance:
- Follow guidelines from bodies like FDA, EMA, WHO, and standards like ISO 14644.
-
Cleanroom Classification:
- Define based on maximum particle counts (ISO Class 5-8).
-
Layout and Design:
- Unidirectional Flow: Prevent cross-contamination.
- Zoning: Establish areas with increasing cleanliness levels.
- Airlocks: Maintain pressure differentials.
- Separate Flows: Distinct entry/exit for personnel and materials.
-
HVAC System:
- HEPA Filtration: Remove particulates.
- Air Changes: Ensure adequate air changes per hour (ACH).
- Pressure Control: Positive pressure in clean zones.
- Temperature/Humidity: Maintain specified levels.
-
Surface Materials:
- Use non-porous, smooth, and easily cleanable materials.
- Coving: Smooth transitions at floor-wall junctions.
-
Equipment and Furnishings:
- Choose designs that minimize dust accumulation and are easy to clean.
-
Lighting:
- Sufficient, non-heat-generating, and easy-to-clean lighting.
-
Personnel and Material Handling:
- Gowning Procedures: Strict protocols for personnel.
- Material Transfer: Use sterile techniques.
-
Cleaning and Maintenance:
- Regular, rigorous cleaning and disinfection schedules.
-
Monitoring and Validation:
- Environmental Monitoring: Regular checks for contaminants.
- Validation: Ensure all processes meet cleanliness standards.
Four Main Grades of Cleanrooms
-
Grade A:
- For high-risk operations (e.g., laminar flow hoods).
- Highest cleanliness standards.
-
Grade B:
- Background for Grade A areas.
- Supports aseptic preparation and filling.
-
Grade C:
- Clean areas for less critical stages (e.g., solution preparation).
-
Grade D:
- Areas for final cleaning and preparatory steps.
Design Example
Advertisements
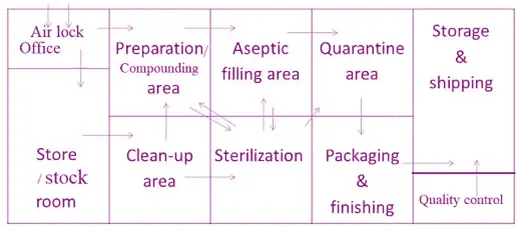
Design Example: Floor Plan Layout
- Gowning Area: Area where personnel change into cleanroom attire.
- Airlock: Maintains pressure differentials between zones.
- Aseptic Core Area: Main cleanroom dedicated to critical operations.
- Material Airlock/Pass-Through: Used for decontaminating materials before entry.
- Support Areas: Includes storage and waste management spaces.
Workflow
-
Entry:
- Separate airlocks for personnel and materials.
-
Processing:
- Conducted in aseptic core with strict protocols.
-
Exit:
- Designated routes for personnel and waste.