Dichlorphenamide is a diuretic used to treat glaucoma and periodic paralysis by inhibiting carbonic anhydrase and reducing fluid buildup.
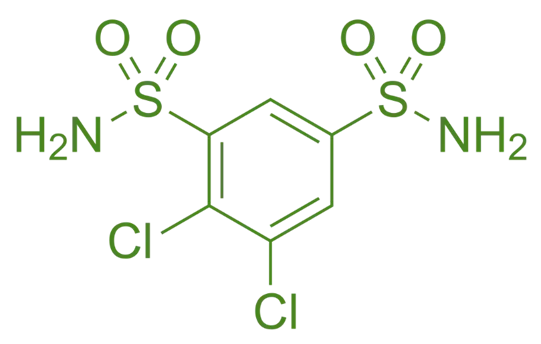
Structure of Dichlorphenamide
- Dichlorphenamide is a sulfonamide derivative with two chlorine atoms attached to the benzene ring and a central sulfonamide group.
- Chemical Formula: C₆H₇Cl₂N₃O₃S₂
Mode of Action
- Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition: Blocks carbonic anhydrase activity, reducing bicarbonate reabsorption in the kidneys.
- Renal Effects: Promotes excretion of bicarbonate, sodium, potassium, and water, leading to diuresis.
- Metabolic Acidosis: Induces mild metabolic acidosis by lowering bicarbonate levels.
Uses
- Glaucoma: Lowers intraocular pressure by decreasing aqueous humor production.
- Epilepsy: Acts as an adjunctive therapy in seizure management.
- Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: Reduces intracranial pressure.
- Diuretic: Used in conditions requiring carbonic anhydrase inhibition.