- Diclofenac inhibits COX enzymes, reducing prostaglandin synthesis for strong anti-inflammatory action.
- It is widely used to treat pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammation.
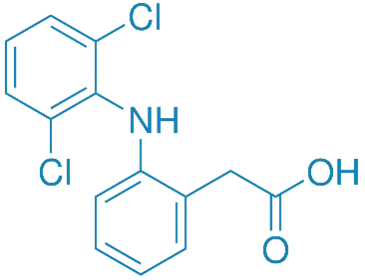
Chemical Formula:
- C₁₄H₁₁Cl₂NO₂
Mechanism of Action:
- Potent COX-2 > COX-1 inhibitor
- Inhibits PG synthesis and may inhibit LOX and lipoxygenase enzymes (minor)
Uses of Diclofenac:
- OA, RA, ankylosing spondylitis
- Post-op pain, dysmenorrhea
- Topical formulations for musculoskeletal pain
Advertisements
Side Effects:
- GI bleeding
- Elevated liver enzymes (hepatotoxicity)
- Cardiovascular risk (dose-related)
SAR Notes:
- Ortho-dichloro substitution increases COX selectivity
- Phenylacetic acid moiety critical for COX binding
- More COX-2 selective than most traditional NSAIDs