- Dihydroergotamine is a medication derived from ergot alkaloids that is primarily used to treat migraine headaches.
- It works by constricting dilated blood vessels in the brain and inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory neuropeptides.
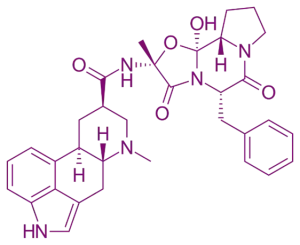
Chemical Structure & Formula:
- An ergot alkaloid with a complex polycyclic structure derived from ergot fungus metabolites, including an ergoline skeleton with several chiral centers.
- Approximate Formula: C₃₃H₄₁N₅O₅

Mechanism of Action:
- Acts as a mixed agonist/antagonist on multiple receptors: partial agonism at 5-HT₁ receptors, antagonism at certain α-adrenergic sites, and dopaminergic effects.
- In migraine treatment, it constricts dilated cranial blood vessels and inhibits trigeminal nerve activation.
Side Effects of Dihydroergotamine:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Muscle cramps
- Dizziness
- Potential peripheral vasospasm (risk of ischemia in susceptible individuals)
Clinical Uses of Dihydroergotamine:
- Employed in the acute treatment of migraine attacks, particularly when triptans are contraindicated.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos