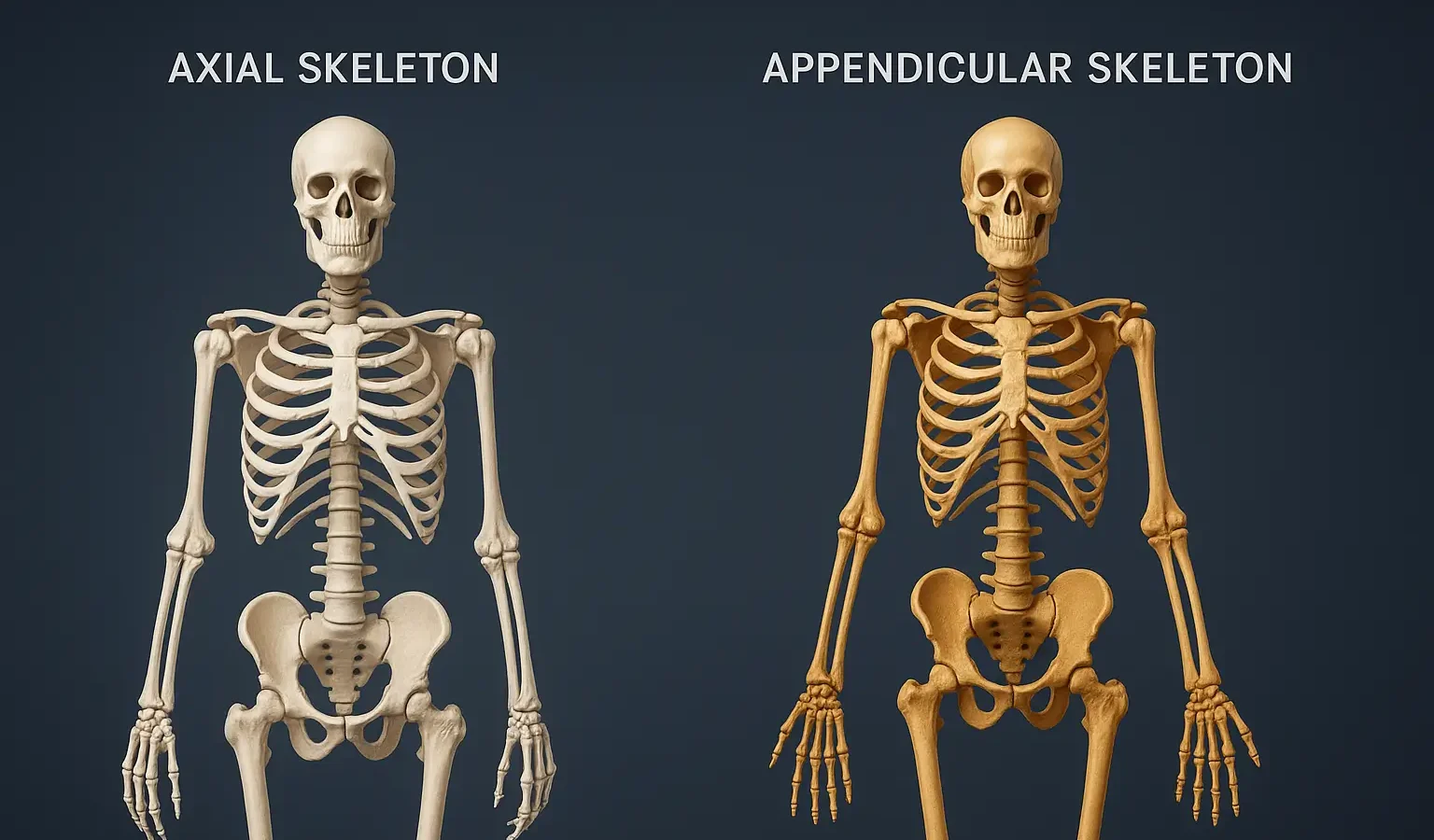
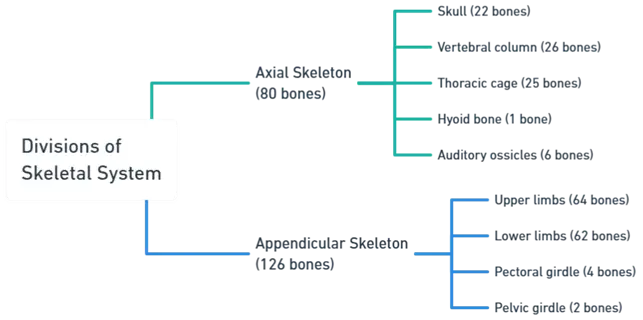
- The Division of skeletal system is divided into two main divisions: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
- The axial skeleton forms the central axis of the body, while the appendicular skeleton consists of the limbs and girdles.
- Here is the Classification and Division of skeletal system, including the names of all bones:
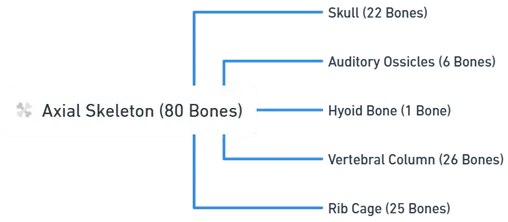
A) Axial Skeleton (80 Bones) (Division of skeletal system)
- The axial skeleton forms the central axis of the body and consists of 80 bones.
- Its primary functions are to protect vital organs in the head, neck, and trunk, and to support the body’s weight.
Advertisements
1. Skull (22 Bones)
-
-
Cranial Bones (8 Bones):
- Frontal (1)
- Parietal (2)
- Occipital (1)
- Temporal (2)
- Sphenoid (1)
- Ethmoid (1)
-
Facial Bones (14 Bones):
- Maxillae (2)
- Zygomatic (2)
- Nasal (2)
- Lacrimal (2)
- Palatine (2)
- Inferior Nasal Conchae (2)
- Vomer (1)
- Mandible (1)
-
-
Features:
- The skull consists of 22 bones, including 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones, joined by immovable joints called sutures.
- The mandible (lower jaw) is the only movable bone in the skull.
-
Functions:
- Protects the brain and forms the structure of the face.
- Provides attachment points for muscles involved in facial expressions and mastication (chewing).
2. Auditory Ossicles (6 Bones)
- Located in each ear:
- Malleus (2)
- Incus (2)
- Stapes (2)
-
Function:
- Transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
3. Hyoid Bone (1 Bone)
- A U-shaped bone in the neck that supports the tongue and is associated with swallowing.
4. Vertebral Column (26 Bones)
-
Cervical Vertebrae (7):
- C1 (Atlas), C2 (Axis), C3-C7
-
Thoracic Vertebrae (12):
- T1-T12
-
Lumbar Vertebrae (5):
- L1-L5
-
Sacrum (1):
- Composed of 5 fused sacral vertebrae
-
Coccyx (1):
- Composed of 3-5 fused coccygeal vertebrae
Advertisements
-
Features:
- The vertebral column is composed of 33 vertebrae, including cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral (fused), and coccygeal (fused) vertebrae.
- Separated by intervertebral discs.
-
Functions:
- Provides support for the body, protects the spinal cord, and serves as an attachment point for muscles and ligaments.
- Allows for flexibility and movement.
5. Rib Cage (25 Bones)
-
Ribs (24 Bones):
- 12 pairs:
- True Ribs (1-7): Attach directly to the sternum via costal cartilage.
- False Ribs (8-10): Attach to the cartilage of the rib above.
- Floating Ribs (11-12): Do not attach to the sternum.
-
Sternum (1 Bone):
- Composed of the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process.
-
Features:
- The rib cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs and the sternum.
-
Functions:
Advertisements
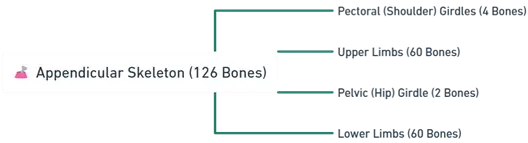
B. Appendicular Skeleton (126 Bones) (Division of skeletal system)
- The appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones and is responsible for mobility.
- It includes the limbs, girdles, and attachment points for limb muscles.
1. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdles (4 Bones)
-
Clavicles (2 Bones):
- Collar bones
-
Scapulae (2 Bones):
- Shoulder blades
-
Features:
- Each pectoral girdle consists of a clavicle and a scapula.
-
Functions:
- Connects the upper limbs to the axial skeleton.
- Provides a stable base for the attachment and movement of upper limb muscles.
2. Upper Limbs (60 Bones)
-
Humeri (2 Bones):
- Upper arm bones
-
Ulnae (2 Bones):
- Medial forearm bones
-
Radii (2 Bones):
- Lateral forearm bones
-
Carpal Bones (16 Bones):
- Wrist bones, 8 in each wrist:
- Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, Hamate
-
Metacarpal Bones (10 Bones):
- Palm bones, 5 in each hand
-
Phalanges (28 Bones):
- Finger bones, 14 in each hand:
- 3 in each finger (Proximal, Middle, Distal), 2 in each thumb (Proximal, Distal)
-
Features:
- The upper limbs consist of the humerus, radius, ulna, carpal bones, metacarpals, and phalanges.
-
Functions:
- Allow for a wide range of movements and dexterity, enabling actions such as grasping, lifting, and manipulating objects.
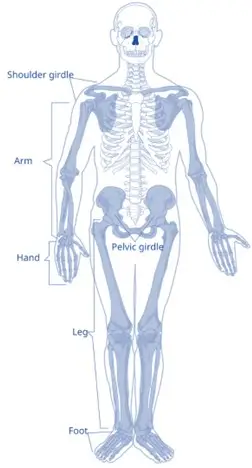
3. Pelvic (Hip) Girdle (2 Bones)
-
Coxal Bones (2 Bones):
- Each formed by the fusion of the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
-
Features:
- The pelvic girdle consists of two coxal bones.
-
Functions:
- Supports the weight of the upper body when sitting and standing.
- Provides attachment points for the lower limbs and protects organs in the pelvic region.
Advertisements
4. Lower Limbs (60 Bones)
-
Femurs (2 Bones):
- Thigh bones
-
Patellae (2 Bones):
- Kneecaps
-
Tibiae (2 Bones):
- Shin bones (medial)
-
Fibulae (2 Bones):
- Calf bones (lateral)
-
Tarsal Bones (14 Bones):
- Ankle bones, 7 in each ankle:
- Talus, Calcaneus, Navicular, Cuboid, Medial Cuneiform, Intermediate Cuneiform, Lateral Cuneiform
- Ankle bones, 7 in each ankle:
-
Metatarsal Bones (10 Bones):
- Foot bones, 5 in each foot
-
Phalanges (28 Bones):
- Toe bones, 14 in each foot:
- 3 in each toe (Proximal, Middle, Distal), 2 in each big toe (Proximal, Distal)
- Toe bones, 14 in each foot:
-
Features:
- The lower limbs consist of the femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsal bones, metatarsals, and phalanges.
-
Functions:
- Provide support, stability, and mobility for the body, enabling actions such as walking, running, jumping, and maintaining balance.