Doxorubicin is an anti-neoplastic antibiotic used in various cancers by intercalating DNA and inhibiting topoisomerase II, blocking cancer cell replication.
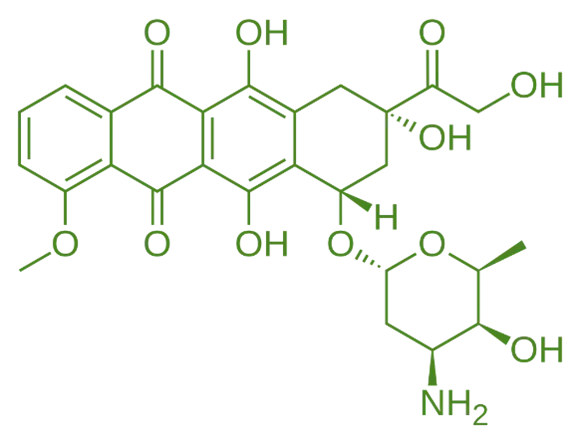
Structure of Doxorubicin
- Doxorubicin, also an anthracycline antibiotic, features a tetracyclic ring structure with a daunosamine sugar moiety and a hydroxyl group.
- Chemical Formula: C₂₉H₂₁NO₁₄
Mode of Action
- DNA Intercalation: Disrupts DNA replication and transcription by inserting between base pairs.
- Topoisomerase II Inhibition: Prevents DNA strand re-ligation, causing DNA breaks.
- Reactive Oxygen Species Generation: Induces oxidative stress leading to cellular damage.
- Apoptosis Induction: Triggers programmed cell death in malignant cells.
Uses
- Breast Cancer: Often used in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents.
- Ovarian Cancer: In combination therapy regimens.
- Lung Cancer: Particularly small cell lung carcinoma.
- Lymphomas: Both Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Leukemias: Including AML and ALL.