Drugs used in Alzheimer’s Disease aim to manage symptoms, slow cognitive decline, and improve daily functioning. These include cholinesterase inhibitors that enhance acetylcholine levels and NMDA receptor antagonists that regulate glutamate activity. By targeting neurotransmitter imbalances, drugs used in Alzheimer’s Disease help improve memory, thinking, and behavior, offering better quality of life for patients.
-
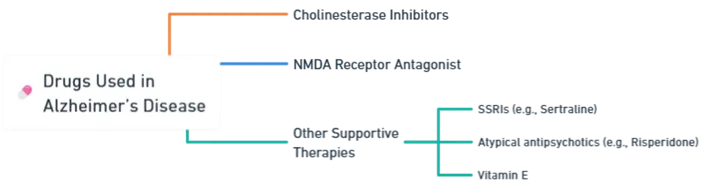
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
- Inhibit acetylcholinesterase, increasing levels of acetylcholine in the brain.
-
Examples:
- Donepezil
- Rivastigmine
- Galantamine
-
Uses:
- Mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease
-
Adverse Effects:
- Gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea)
- Bradycardia, syncope
- Insomnia
-
NMDA Receptor Antagonist
- Memantine
- Blocks pathological NMDA receptor activation by glutamate, which may prevent excitotoxic neuronal damage.
-
Uses:
- Moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease
- Often used in combination with donepezil
-
Adverse Effects:
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Headache
-
Other Supportive Therapies
- SSRIs (e.g., sertraline): For depression
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., risperidone): For agitation and psychosis (used with caution)
- Vitamin E: Antioxidant, possible modest benefit
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos

