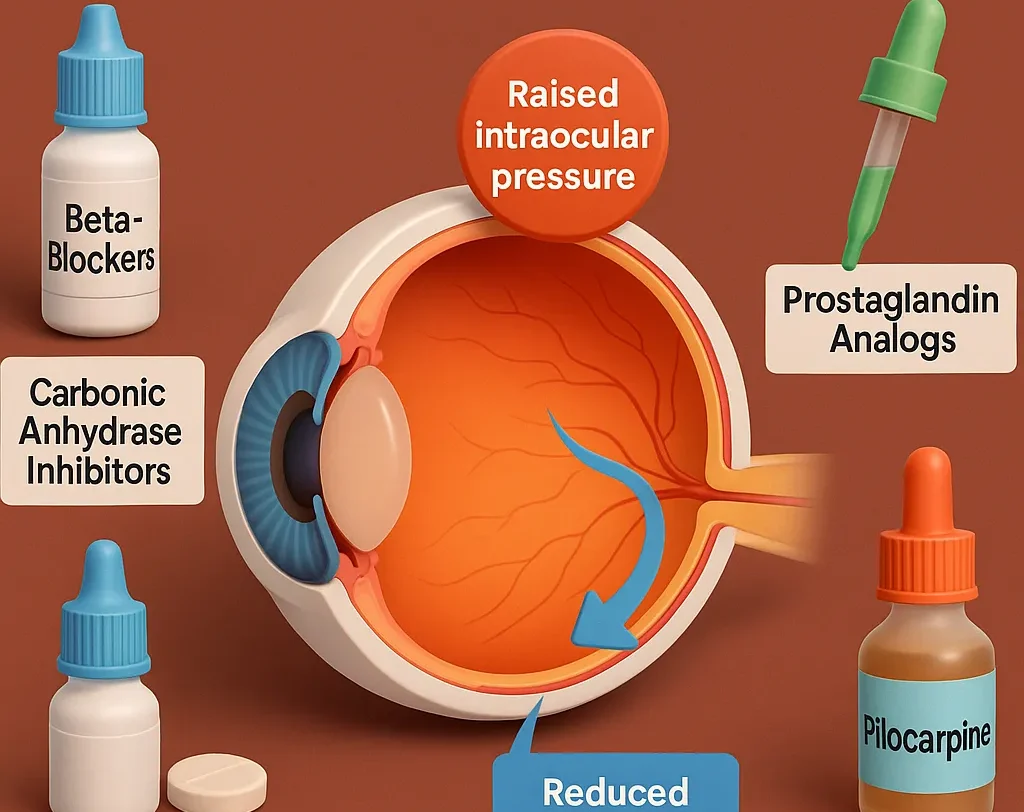
Drugs for glaucoma include beta-blockers, prostaglandins, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors to lower eye pressure.
Pharmacological Goal:
To reduce intraocular pressure by:
- Decreasing aqueous humor production, or
- Increasing aqueous humor outflow
Classes of Drugs Used in Glaucoma:
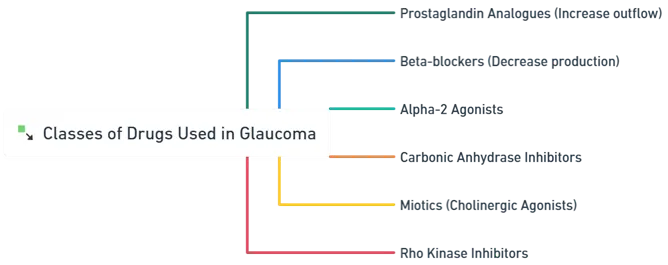
-
Prostaglandin Analogues (Increase outflow)
- Latanoprost, Travoprost, Bimatoprost
- Mechanism: Increase uveoscleral outflow
- Side Effects: Iris pigmentation, eyelash growth
-
Beta-blockers (Decrease production)
- Timolol, Betaxolol
- Mechanism: Block beta receptors in ciliary body
- Side Effects: Bradycardia, bronchospasm (due to systemic absorption)
-
Alpha-2 Agonists
- Brimonidine, Apraclonidine
- Mechanism: Decrease aqueous production and increase outflow
- Side Effects: Dry mouth, fatigue
-
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
- Topical: Dorzolamide
- Oral: Acetazolamide
- Mechanism: Inhibit enzyme carbonic anhydrase → reduces aqueous production
- Side Effects: Metabolic acidosis, kidney stones (especially with oral form)
-
Miotics (Cholinergic Agonists)
- Pilocarpine
- Mechanism: Constricts pupil, opens trabecular meshwork → increases outflow
- Clinical Use: Acute angle-closure glaucoma
- Side Effects: Headache, blurred vision
-
Rho Kinase Inhibitors
- Netarsudil
- Mechanism: Increases trabecular outflow
- Newer class with expanding clinical use
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos