- Effect of Electrolytes on Colloidal Stability explains how ions alter charge, causing coagulation or stability.
- Effect of Electrolytes on Colloidal Stability is key in pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and food systems.
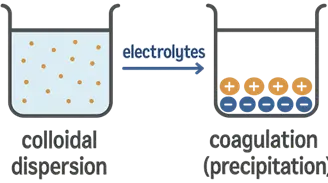
- Electrolytes play a crucial role in determining colloidal stability by influencing the surface charge and electric double layer surrounding colloidal particles.
Advertisements
1. Coagulation and Double Layer Compression
- Electrolyte ions neutralize the surface charge of colloidal particles.
- This leads to:
- Reduction in zeta potential
- Compression of the electric double layer
- Weakened electrostatic repulsion between particles
- Result: Particles come closer together, leading to flocculation (aggregation) or coagulation (precipitation).
- Pharmaceutical relevance:
- Excessive electrolytes in colloidal drug formulations can lead to instability.
- In parenteral preparations, this can pose serious risks (e.g., embolism).
Advertisements
2. Schulze–Hardy Rule
- The coagulating power of an electrolyte increases with the valency of the counter-ion.
- Higher-valency ions are more efficient at neutralizing colloidal charges.
- For negatively charged colloids:
- Al³⁺ > Ca²⁺ > Na⁺
- Importance:
- Helps in predicting and controlling colloidal stability in formulations and industrial processes.
- For negatively charged colloids:
3. Critical Coagulation Concentration (CCC)
- CCC is the minimum concentration of an electrolyte required to cause coagulation of colloidal particles.
- A lower CCC means:
- Stronger electrolyte effect
- Greater tendency to destabilize the colloid
Advertisements