- Elastic and Plastic Deformation explains temporary vs permanent shape changes in materials under stress.
- Elastic and Plastic Deformation is key in material science for strength, durability, and design.
- When an external force is applied to a solid, it may change shape or size.
- This is called deformation.
- It can be elastic or plastic depending on the extent of the force and the material properties.
- Solids deform in two main ways under stress:
Elastic Deformation
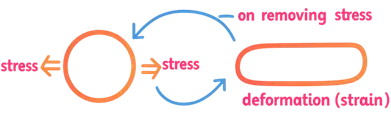
- Definition: A temporary deformation. The material returns to its original shape after removal of stress.
- Cause: Stretching of interatomic bonds.
- Behavior: Linear stress-strain relationship (Hooke’s Law).
- Example in pharmaceutics: Microcrystalline cellulose exhibits predominantly elastic behavior.
Advertisements
Hooke’s Law:
$\sigma = E \cdot \varepsilon$
- Where:
- E = Elastic modulus or Young’s modulus
Advertisements
Plastic Deformation
- Definition: A permanent deformation. The material does not return to its original shape after stress is removed.
- Cause: Irreversible movement of atoms or particles.
- Important in powder compression: Materials must undergo some plastic flow to form solid, coherent tablets.
- Example: Starch and calcium phosphate show more plastic deformation.

Advertisements