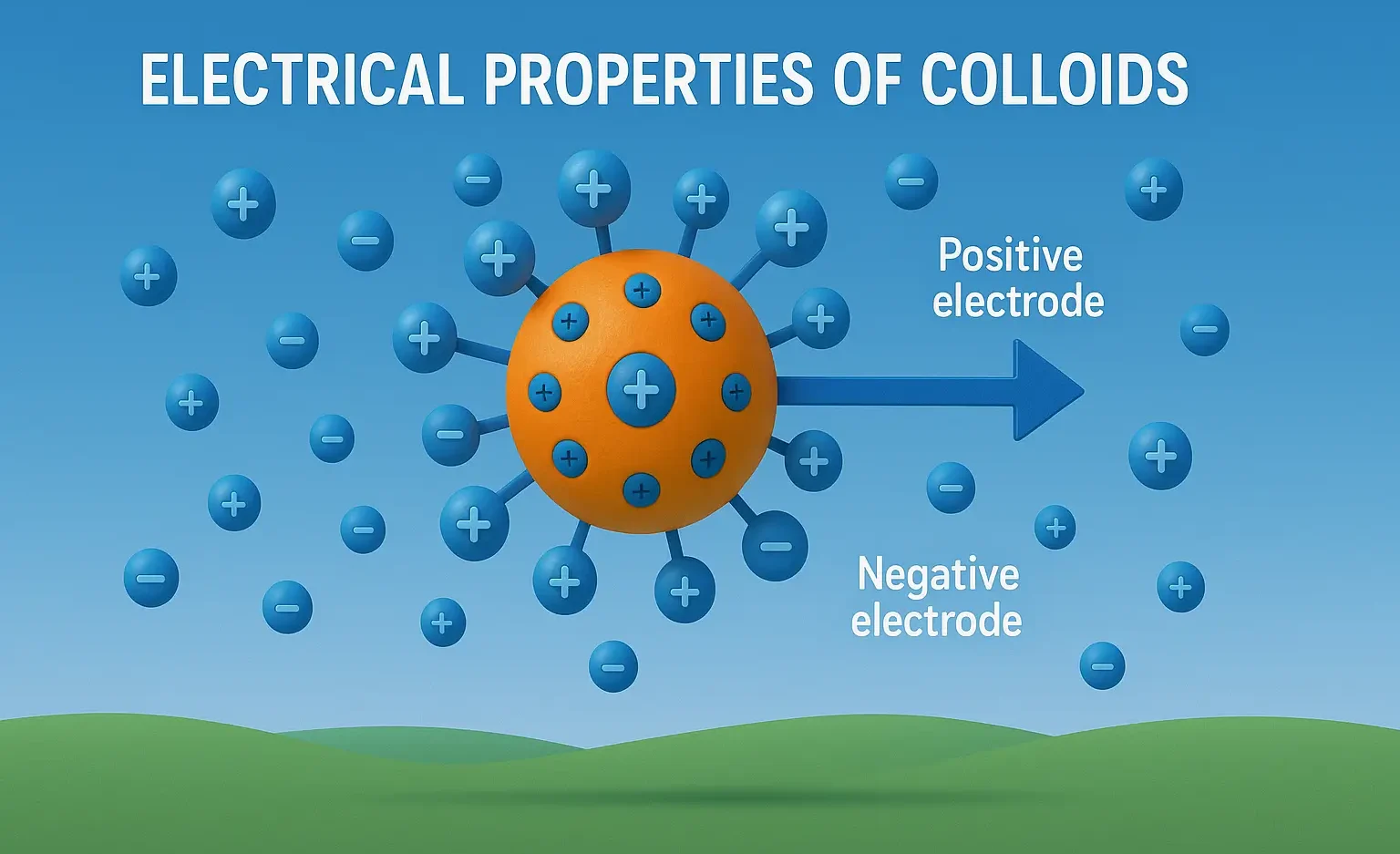
- Electrical Properties of Colloids explain charge, electrophoresis, and electro-osmosis in dispersions.
- Colloidal particles typically carry a surface charge when dispersed in a medium.
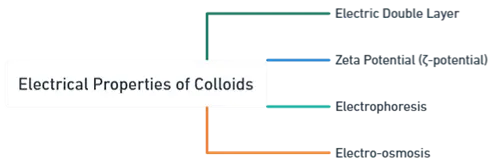
- Electrical Properties of Colloids determine stability and behavior of colloidal systems.
- This charge influences their stability, interactions, and movement under electric fields.
The key electrical properties include:
Advertisements
1. Electric Double Layer
- Colloidal particles acquire a surface charge that attracts oppositely charged ions, forming an electric double layer:
- Fixed layer: Tightly bound counterions directly attached to the particle surface.
- Diffuse layer: Loosely associated, mobile ions surrounding the fixed layer.
- This double layer affects interparticle forces and plays a major role in colloidal stability.
2. Zeta Potential (ζ-potential)
- Zeta potential is the electrical potential at the shear plane between the fixed and diffuse layers of the electric double layer.
- It is a key indicator of colloidal stability:
- High ζ-potential (positive or negative): Strong electrostatic repulsion → Stable colloid
- Low ζ-potential: Weak repulsion → Particle aggregation or flocculation
- Pharmaceutical relevance: Zeta potential measurements are crucial for evaluating and optimizing the stability of formulations.
Advertisements
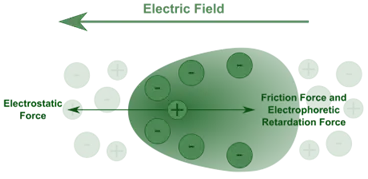
3. Electrophoresis
- Refers to the movement of charged colloidal particles under the influence of an electric field.
- The direction of movement reveals the nature of the surface charge (positive or negative).
- It is used to study particle charge, mobility, and helps in formulation optimization.
Advertisements
4. Electro-osmosis
- Describes the movement of the dispersion medium (not the particles) under an electric field, typically when particles are immobilized (e.g., in a filter bed).
- This is the opposite of electrophoresis.
- It is useful in analyzing surface charge characteristics and ionic interactions at interfaces.