- An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a non-invasive diagnostic test that records the electrical activity of the heart over time.
- It is commonly used to detect and analyze heart-related problems, including abnormal rhythms, inadequate blood flow, and structural issues.
How an ECG Works:
- The ECG measures the electrical changes on the skin produced by the depolarization and repolarization of the heart muscle during each cardiac cycle.
- Electrodes are placed on the chest, arms, and legs to detect these signals, which are then transmitted to an ECG machine.
- The machine displays the electrical signals as a series of waves on a screen or on printed paper.
Advertisements
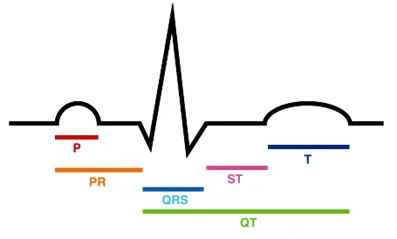
Components of an ECG Tracing:
-
P Wave:
- Represents atrial depolarization, the process when the atria contract and pump blood into the ventricles.
-
QRS Complex:
- Represents ventricular depolarization, which occurs when the ventricles contract and pump blood out of the heart.
- It consists of:
- Q wave: A small downward deflection.
- R wave: A tall upward deflection.
- S wave: A small downward deflection following the R wave.
-
T Wave:
- Represents ventricular repolarization, the phase when the ventricles recover from contraction and prepare for the next cardiac cycle
Advertisements
Clinical Significance of Electrocardiogram:
- By analyzing the ECG tracing, healthcare providers can assess:
- Heart rate and rhythm
- Electrical conduction pathways
- Cardiac function
Conditions Detected by ECG:
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms.
- Myocardial infarction: Heart attack.
- Ischemia: Reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Cardiomyopathy: Disease of the heart muscle.
- Heart valve problems: Issues with the function of the heart valves.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the sac around the heart.
- Electrolyte imbalances: Abnormalities in the body’s electrolytes, such as potassium or calcium.
Advertisements
Procedure and Benefits:
- An ECG is a quick, painless, and low-risk
- It provides essential information about heart health and is often done as part of a routine physical exam or to investigate symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations.