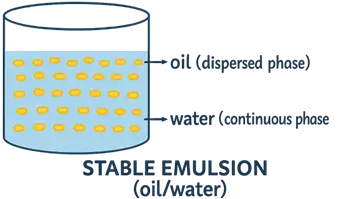
Definition of Emulsions:
- An emulsion is a biphasic (two-phase) system consisting of two immiscible liquids, where one liquid (the dispersed phase) is finely dispersed in the form of droplets throughout the other (the continuous phase), stabilized by an emulsifying agent.
Classification of Emulsions
Emulsions can be classified into four types:
Advertisements
-
Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsion:
- Oil droplets dispersed in water (e.g., milk).
-
Water-in-Oil (W/O) Emulsion:
- Water droplets dispersed in oil (e.g., butter).
-
Multiple Emulsion:
- A combination such as W/O/W or O/W/O, where droplets themselves contain smaller droplets of another emulsion.
-
Microemulsion:
- Thermodynamically stable, transparent emulsion with droplet sizes typically in the range of 10–100 nm.
Examples in Pharmaceuticals:
- Oral emulsion (e.g., castor oil emulsion)
- Topical emulsion (e.g., creams and lotions)
- Parenteral emulsion (e.g., intravenous lipid emulsion)
Advertisements
Key Components:
- Dispersed phase: The internal phase (droplets)
- Continuous phase: The external phase
- Emulsifying agent: Surfactants that stabilize the emulsion
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements