- Ephedrine is a naturally occurring alkaloid and stimulant derived from the plant Ephedra.
- It acts as both a sympathomimetic agent and bronchodilator, stimulating the central nervous system by increasing the activity of norepinephrine.
- Medically, ephedrine is used to treat conditions such as hypotension, nasal congestion, and bronchospasm in asthma.
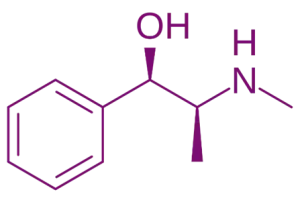
Chemical Structure & Formula
- Chemical Formula: C₁₀H₁₅NO
- Structure:

Mechanism of Action (Detailed)
- Directly activates α1, α2, β1, and β2 receptors.
- Increases norepinephrine release → Enhances sympathetic activity.
- Crosses the blood-brain barrier → CNS stimulation.
Physiological Effects
-
Cardiovascular:
- Increases BP & HR (α1 and β1 effects).
- Vasoconstriction (α1 effect).
-
Respiratory:
- Bronchodilation (β2 effect, but weaker than salbutamol).
-
CNS:
- Increases alertness, reduces fatigue.
- Mild euphoria & appetite suppression.
Advertisements
Side Effects of Ephedrine
- Hypertension & Tachycardia
- Restlessness, Insomnia
- Urinary retention
Clinical Uses of Ephedrine
- Nasal decongestant
- Hypotension (during anesthesia)
- Mild bronchodilator (historically used for asthma, now replaced by β2 agonists)