- Esmolol is a short-acting, selective beta-1 adrenergic receptor blocker (beta-blocker) primarily used to manage rapid heart rates and hypertension, especially in acute care settings.
- Its rapid onset and very short half-life, esmolol is typically administered intravenously and allows for precise control of heart rate in situations like supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation.
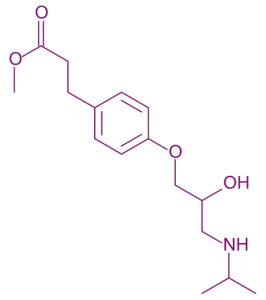
Chemical Structure & Formula:
- An ultra-short-acting β₁-selective blocker formulated as an ester prodrug, with the ester moiety key to its rapid hydrolysis.
- Approximate Formula: C₁₅H₂₄N₂O₃

Advertisements
Mechanism of Action:
- Rapidly blocks β₁ receptors, lowering heart rate and myocardial contractility.
- Quickly metabolized by plasma esterases, resulting in a very short duration of action.
Side Effects of Esmolol:
- Hypotension
- Bradycardia
- Injection site reactions when administered intravenously
Advertisements
Advertisements
Clinical Uses of Esmolol:
- Ideal for acute control of supraventricular tachycardia, intraoperative tachyarrhythmias, and other scenarios requiring fast, titratable beta blockade.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements