Etidocaine is a long-acting amide local anesthetic used for surgical anesthesia and nerve blocks.
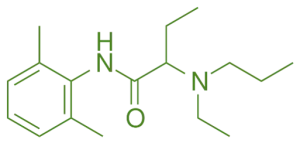
Structure of Etidocaine
- It is an amide-type local anesthetic with an extended diethylaminoethyl side chain, providing prolonged anesthetic effects.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₅H₂₈N₂O
Mode of Action
- Sodium Channel Inhibition: Blocks voltage-gated sodium channels, preventing nerve impulse propagation.
- Membrane Stabilization: Reduces nerve excitability by enhancing membrane stability.
Uses
- Local Anesthesia: Used in dental procedures, minor surgeries, and obstetric anesthesia for prolonged numbness.
- Topical Preparations: Applied to skin and mucous membranes for extended local pain relief.
- Infiltration Anesthesia: Injected to provide sustained localized anesthesia during medical procedures.
Side Effects of Etidocaine
- Local Reactions: Redness, swelling, or irritation at the injection site.
- Systemic Toxicity: Potential CNS excitation (e.g., seizures) and cardiovascular effects (e.g., arrhythmias) with excessive doses.

