Excretion of drugs is the process of eliminating drugs and metabolites mainly via kidneys, bile, or lungs.
Excretion of Drugs
- Excretion is the process by which the drug or its metabolites are removed from the body.
-
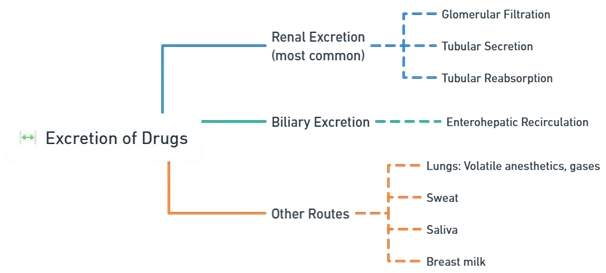
Renal Excretion (most common)
- Glomerular Filtration: Depends on the free drug fraction in plasma (unbound drug is freely filtered).
- Tubular Secretion: Active transport in the proximal tubule (e.g., secretion of acidic drugs by organic anion transporters, basic drugs by organic cation transporters).
- Tubular Reabsorption: Passive diffusion of lipid-soluble unionized drugs from the renal tubule back into the bloodstream.
-
Biliary Excretion
- Drugs or metabolites secreted into bile, then into the intestine.
- Enterohepatic Recirculation: Some drugs get reabsorbed from the gut, prolonging their half-lives (e.g., certain oral contraceptives).
-
Other Routes