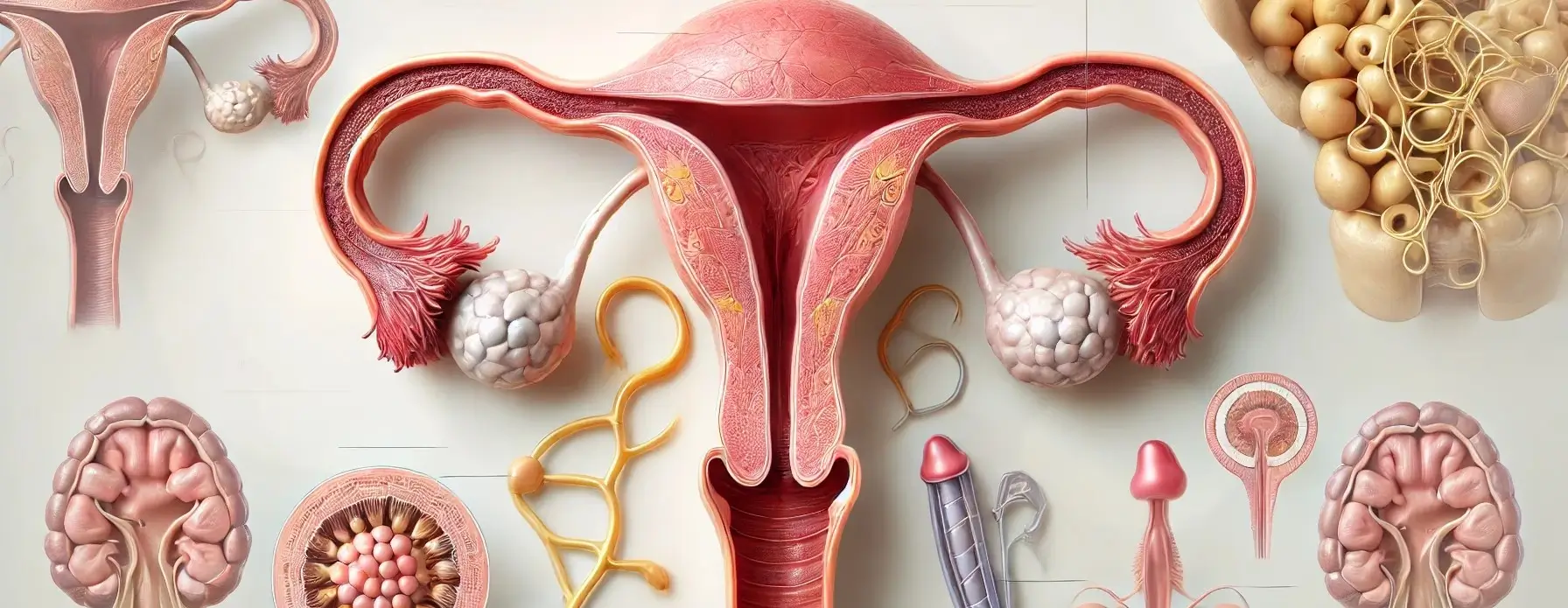
- The female reproductive system consists of internal and external organs that function together for reproduction, hormone regulation, and the menstrual cycle.
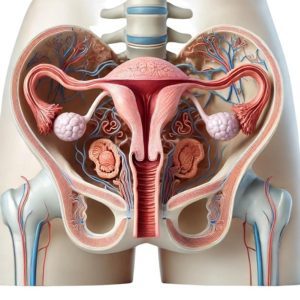
These organs are categorized into primary and accessory
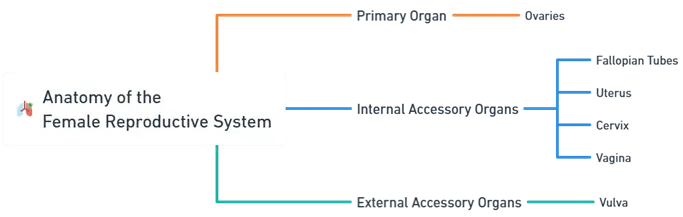
Primary Organ:
Ovaries:
-
- The primary reproductive organs in female reproductive system responsible for producing ova (eggs) and secreting the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
- Each ovary contains thousands of follicles, which are small sacs containing immature eggs. During each menstrual cycle, one or more follicles mature, and one egg is released during ovulation.
- Position:
- Located on either side of the lower abdomen, adjacent to the lateral pelvic wall.
- Structure:
- Almond-shaped organs containing numerous follicles (small sacs that contain immature eggs).
- Ovarian stroma, the connective tissue, contains blood vessels, nerves, and hormone-producing cells.
- Function:
Advertisements
Accessory Organs:
Internal Accessory Organs
1. Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts):
- Two narrow tubes that extend from the ovaries to the uterus.
- Each tube has finger-like projections called fimbriae that guide the egg from the ovary into the tube.
- Fertilization typically occurs here.
- Position:
- Extending from the ovaries to the uterus.
- Structure:
- Lined with ciliated epithelial cells and smooth muscle.
- The fimbriae are at the end near the ovary to help capture the egg.
- Function:
- To transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
- To provide a suitable environment for fertilization.
- Position:
2. Uterus (Womb):
- A muscular, pear-shaped organ that houses and nourishes a developing foetus during pregnancy.
- The endometrium (inner lining of the uterus) thickens during the menstrual cycle to prepare for pregnancy, and if fertilization does not occur, the endometrium is shed during menstruation.
- Position:
- Located in the lower abdomen between the bladder and rectum.
- Structure:
- Composed of three layers:
- Endometrium (inner lining)
- Myometrium (middle muscular layer)
- Perimetrium (outer serous layer)
- Composed of three layers:
- Function:
- To house and nourish a developing foetus during pregnancy.
- To shed its inner lining during menstruation if fertilization does not occur.
- Position:
3. Cervix:
- The lower, narrow part of the uterus that connects it to the vagina.
- Contains a small opening called the os that allows for the passage of sperm into the uterus and the exit of menstrual blood.
- During childbirth, the cervix dilates to allow the baby to pass through the birth canal.
4. Vagina:
- A muscular, elastic canal that extends from the cervix to the vulva.
- Serves multiple functions: it is the receptacle for the penis during sexual intercourse, the passage for menstrual blood to exit the body, and the birth canal during childbirth.
- Position:
- Extends from the cervix (lower part of the uterus) to the vulva.
- Structure:
- Composed of three layers:
- Mucosal layer (inner)
- Muscular layer (middle)
- Fibrous layer (outer)
- The vaginal walls can expand and contract to aid in childbirth.
- Composed of three layers:
- Function:
- Receptacle for the penis during sexual intercourse.
- Passage for menstrual blood to exit the body.
- Birth canal during childbirth.
- Position:
External Accessory Organs
Vulva:
- The external female genitalia, including:
- Mons pubis: A fatty, rounded area over the pubic bone, covered with pubic hair.
- Labia majora: Large, fleshy folds that surround the vaginal opening.
- Labia minora: Smaller inner folds that protect the clitoris and urethra.
- Clitoris: A small, sensitive organ involved in sexual arousal and pleasure.
- Vaginal opening: Allows for the entrance of the penis during intercourse, the exit of menstrual blood, and childbirth.
Advertisements