- Fentanyl Citrate is a synthetic opioid acting on μ-receptors, offering strong pain relief with fast onset.
- It provides rapid, potent analgesia for surgery, cancer pain, and anesthesia.
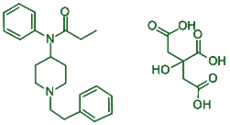
Chemical Formula:
- C₂₂H₂₈N₂O·C₆H₈O₇
Mechanism of Action:
- Full μ-opioid receptor agonist
- 50–100× more potent than morphine
- High lipophilicity → rapid onset and short duration
Advertisements
Uses of Fentanyl Citrate:
- Severe acute pain
- Surgical anesthesia (IV, transdermal)
- Breakthrough cancer pain (lozenges, sprays)
- Epidural analgesia
Side Effects:
- Profound respiratory depression
- Chest wall rigidity (with rapid IV)
- Sedation
- Nausea, bradycardia
SAR of Fentanyl:
-
Anilidopiperidine core:
- Required for strong μ-receptor binding.
-
Phenyl ring on piperidine:
- Enhances binding via π-π stacking with receptor.
-
Amide linkage (anilide):
- Stabilizes the conformation of the molecule, critical for activity.
-
Lipophilicity:
- High lipid solubility → rapid onset and short duration (suitable for IV use).
-
Flexible side chain:
- Allows proper receptor fit.
-
N-phenethyl group:
- Strongly enhances μ-receptor affinity and potency.
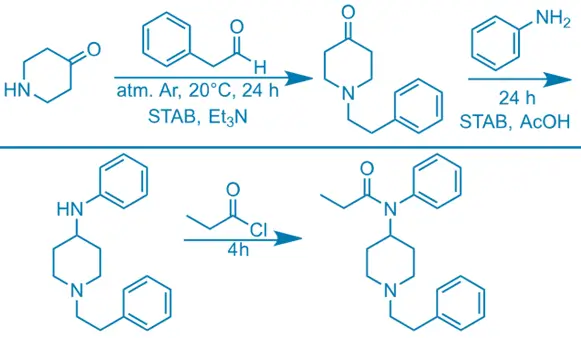
Synthesis of Fentanyl:
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements

