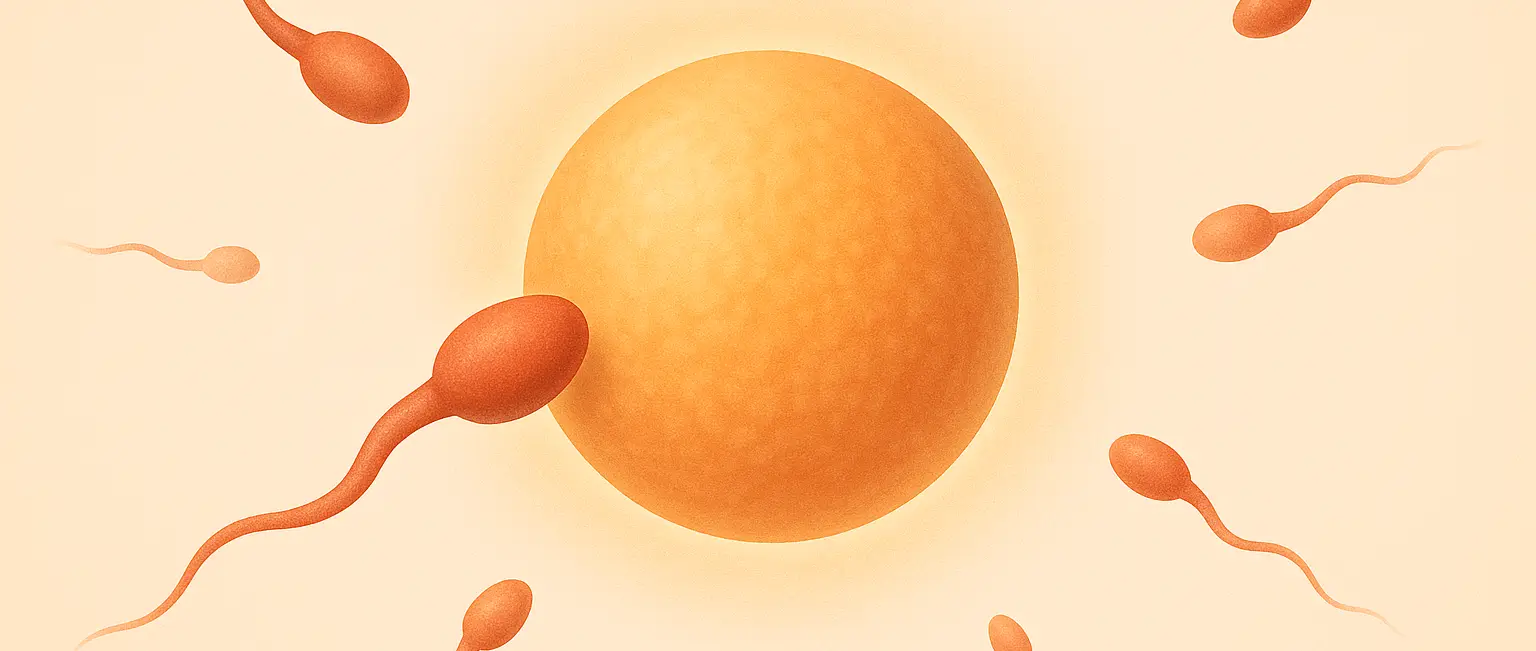
- Fertilization is the process by which a sperm cell from a male combine with an egg cell from a female, resulting in a single-celled zygote, the first stage of embryonic development.
- Fertilization can be divided into several phases:
1. Sperm Migration and Capacitation:
- After ejaculation, sperm swim towards the egg in the fallopian tube.
- During migration, sperm undergo capacitation, which removes glycoproteins from their surface, enhancing their ability to bind to the egg’s outer layer (zona pellucida).
2. Acrosome Reaction:
- Upon reaching the zona pellucida, the sperm’s acrosome (a vesicle at the tip of the sperm head).
- Releases enzymes that digest this outer layer, allowing the sperm to penetrate the egg.
3. Sperm-Egg Binding and Fusion:
- The sperm binds to receptors on the egg’s plasma membrane, leading to fusion.
- The sperm’s nucleus enters the egg’s cytoplasm, leaving behind its tail and mitochondria.
Advertisements
4. Cortical Reaction:
- Once the sperm enters the egg, cortical granules release enzymes that harden the zona pellucida.
- It prevents additional sperm from entering (polyspermy).
5. Pronuclear Fusion and Zygote Formation:
- The male and female pronuclei fuse, combining genetic material to form a zygote, marking the completion of fertilizing.

6. Egg Activation:
- The egg’s metabolic processes activate, preparing the zygote for cell division and embryonic development.
7. Implantation:
- A few days after fertilizing, the multicellular blastocyst implants into the uterine wall, beginning the next stage of development.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements