- First-Order Reactions are vital in drug stability, absorption, and pharmacokinetic studies.
- Definition: Rate of degradation is proportional to the concentration of the drug.
- Rate law:
Derivation:
Separate variables:
$\text{Rate} = -\frac{d[A]}{dt} = k[A]$
Integrate both sides:
$\frac{d[A]}{[A]} = -k \, dt$
- Integrated form:
$\int_{[A]_0}^{[A]} \frac{d[A]}{[A]} = -k \int_{0}^{t} dt$
$\ln [A] – \ln [A]_0 = -kt$
$\ln\!\left(\frac{[A]}{[A]_0}\right) = -kt$
- Graph: $\text{Plot of } \ln [A] \text{ vs. time = straight line with slope } -k$
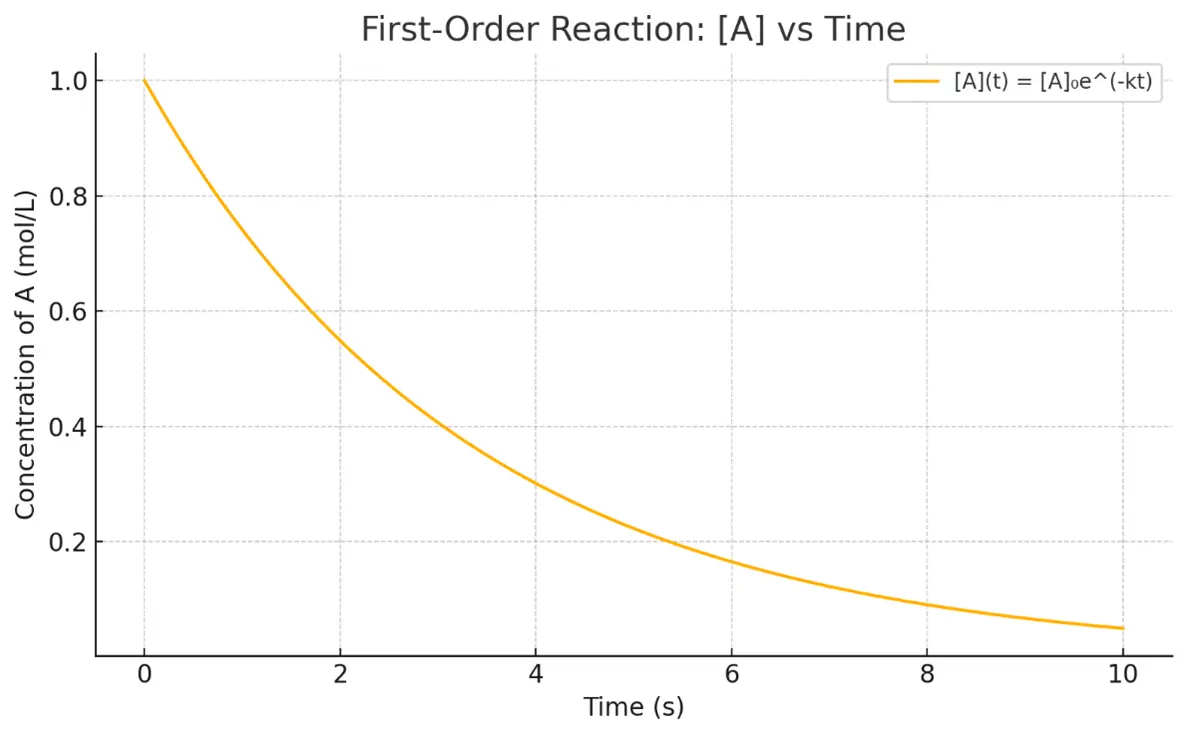
$\ln [A]_t = \ln [A]_0 – kt \quad \text{or} \quad [A]_t = [A]_0 e^{-kt}$
Features:
- Constant fraction of drug degrades per unit time.
- Half-life is constant:
$t_{1/2} = \frac{0.693}{k}$
- Shelf life:
$t_{90} = \frac{0.105}{k}$