Floxuridine is an anti-neoplastic antimetabolite used mainly in colorectal cancer by inhibiting DNA synthesis in tumor cells.
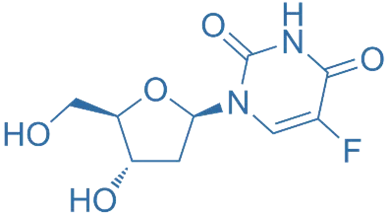
Structure of Floxuridine
- FUDR is a fluorinated pyrimidine analog with the following structural features:
- Uracil Base: Similar to uracil.
- Fluorine Atom: Substituted at the 5-position.
- Ribose Sugar: Attached to the uracil base, forming a nucleoside.
- Chemical Formula: C₆H₆FN₂O₆
Mode of Action
- Floxuridine acts as an antimetabolite by:
- Inhibition of Thymidylate Synthase: Prevents dTMP synthesis, essential for DNA replication.
- Incorporation into DNA and RNA: Disrupts nucleic acid function and structure.
- Induction of Apoptosis: Causes cytotoxicity in rapidly dividing cells.
Uses
- Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Often administered via hepatic artery infusion.
- Liver Metastases: Targeted therapy for liver tumors.
- Pancreatic Cancer: As part of combination chemotherapy regimens.

