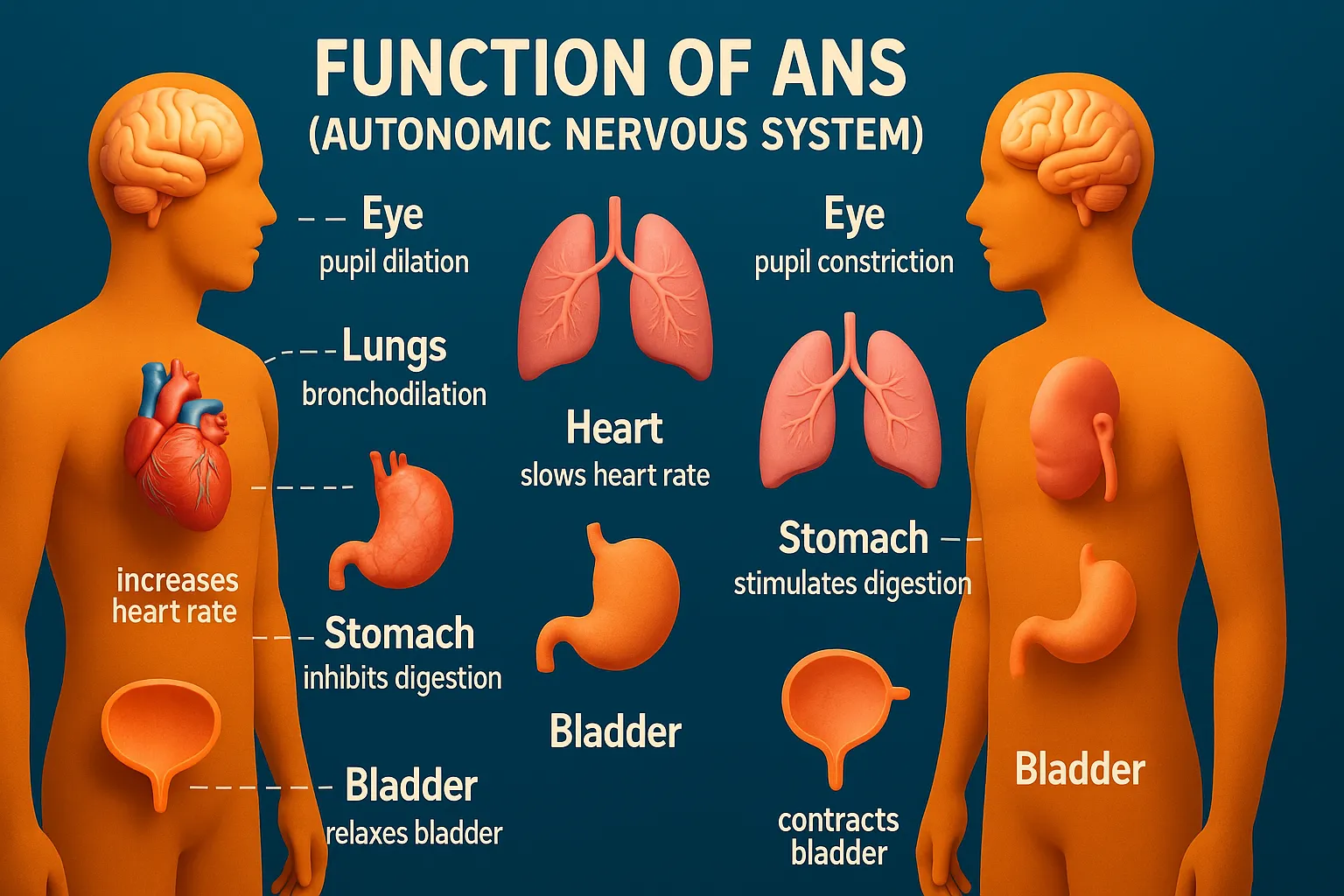
The autonomic nervous system regulates vital functions like heart rate, digestion, respiration, and glandular activity.
-
Sympathetic Nervous System (Fight or Flight)
- Prepares the body for emergency or stressful situations.
-
Physiological effects:
- Heart: ↑ heart rate and force of contraction (β1)
- Blood vessels: Vasoconstriction (α1) in skin and viscera; vasodilation (β2) in skeletal muscle
- Lungs: Bronchodilation (β2)
- Pupils: Dilation (mydriasis) via radial muscle contraction (α1)
- GI tract: ↓ motility and secretions (α, β)
- Urinary bladder: Relaxation of detrusor (β3), contraction of sphincter (α1)
- Liver: ↑ glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis (β2)
- Adrenal medulla: Releases epinephrine and norepinephrine into circulation (via chromaffin cells activated by ACh on nicotinic receptors)
-
Parasympathetic Nervous System (Rest and Digest)
- Promotes maintenance activities and conserves energy.
-
Physiological effects:
- Heart: ↓ heart rate (M2)
- Lungs: Bronchoconstriction and ↑ secretions (M3)
- GI tract: ↑ motility and secretions (M3)
- Urinary bladder: Contraction of detrusor, relaxation of sphincter (M3)
- Pupils: Constriction (miosis) via circular muscle (M3)
- Lacrimal/salivary glands: ↑ secretion (M3)