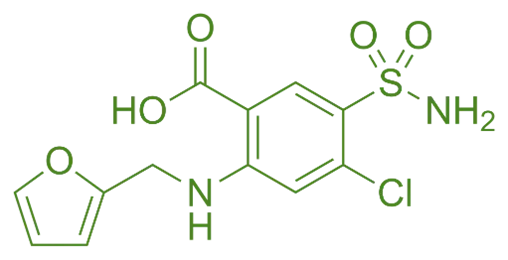
Furosemide is a loop diuretic used to treat edema and hypertension by promoting rapid excretion of sodium, chloride, and water from the kidneys.
Structure of Furosemide
- Furosemide is a sulfonamide derivative belonging to the loop diuretic class, characterized by a benzothiazine structure with a furan ring and a sulfonamide group.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₅H₁₉ClN₂O₅S₂
Mode of Action
- Loop of Henle Inhibition: Inhibits the Na⁺/K⁺/2Cl⁻ symporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle.
- Sodium, Potassium, Chloride Excretion: Promotes excretion of these ions, leading to significant diuresis.
- Calcium and Magnesium Retention: Increases the reabsorption of calcium and magnesium, reducing the risk of kidney stones.
Uses
- Edema: Effective in managing edema associated with congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and renal disease.
- Hypertension: Used to lower blood pressure by reducing blood volume.
- Hypercalcemia: Treats elevated calcium levels by promoting its excretion.
- Acute Pulmonary Edema: Provides rapid diuresis to alleviate fluid accumulation in the lungs.
- Hyponatremia: Manages low sodium levels by promoting sodium excretion.
Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
- Benzothiazine Core: Essential for loop diuretic activity by targeting the Na⁺/K⁺/2Cl⁻
- Furan Ring: Enhances binding affinity and potency by facilitating proper orientation for transporter inhibition.
- Sulfonamide Groups: Critical for interaction with the transporter; substitutions can affect potency and duration of action.
- Chlorine Substituent: Increases lipophilicity, enhancing membrane permeability and bioavailability.
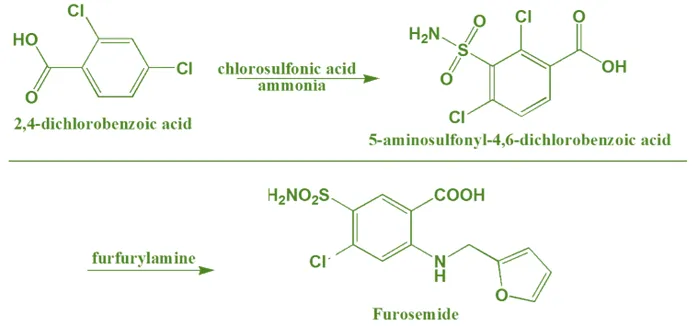
Synthesis