- Glycogen metabolism is a vital process in the human body, responsible for the storage and release of glucose, which is a primary source of energy.
- This process includes two main pathways: glycogenesis (the synthesis of glycogen) and glycogenolysis (the breakdown of glycogen).
- Abnormalities in these processes can lead to glycogen storage diseases (GSD), a group of inherited metabolic disorders.
- Below is a detailed explanation of glycogen metabolism pathways followed by an overview of notable GSD types.
Glycogen Metabolism Pathways
-
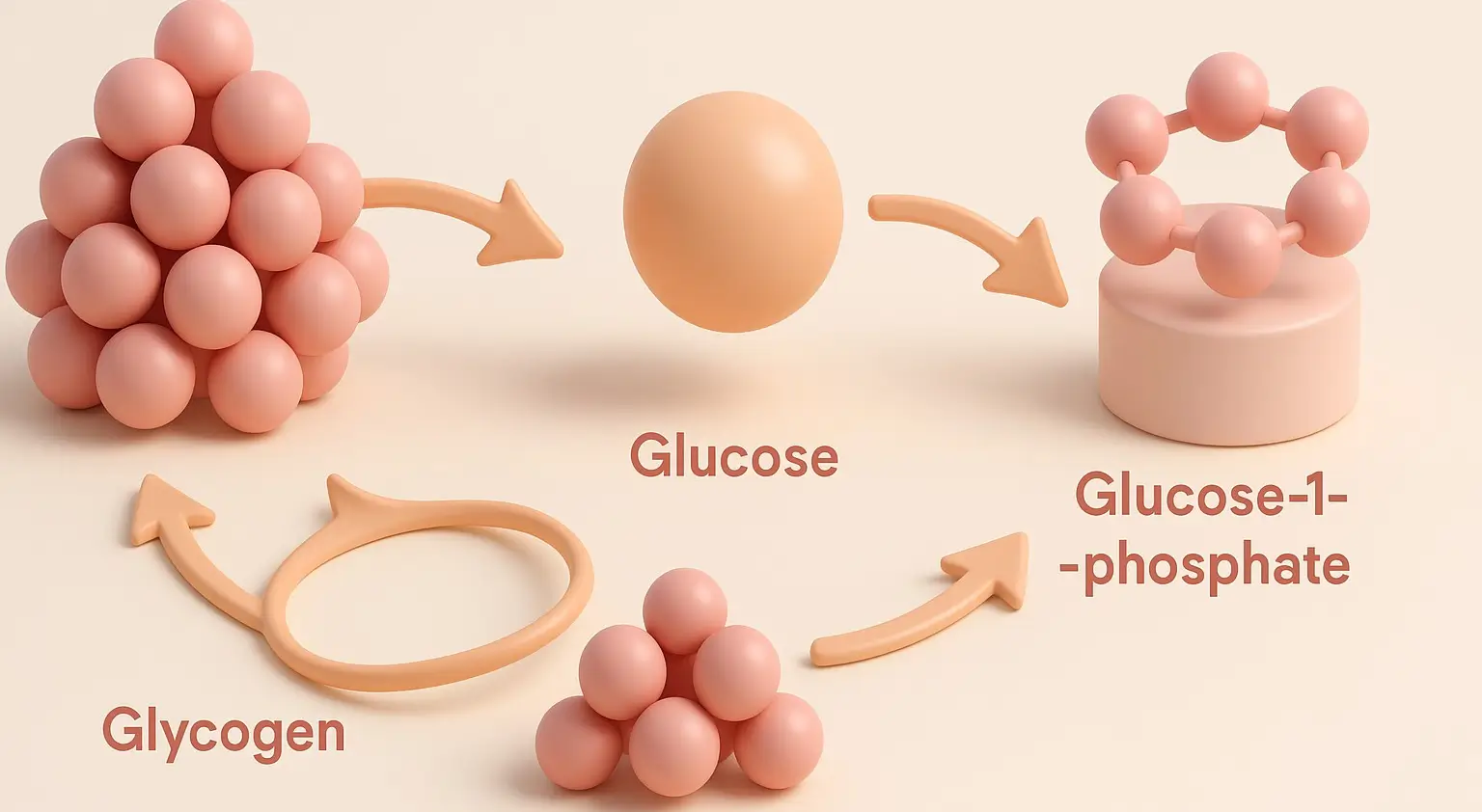
Glycogenesis (Synthesis of Glycogen)
- Purpose: Converts glucose into glycogen for storage, mainly in the liver and muscles.
-
Key Steps:
- Glucose to G6P: Phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) by hexokinase (or glucokinase in the liver).
- Isomerization: G6P isomerized to glucose-1-phosphate (G1P) by phosphoglucomutase.
- UDP-Glucose Formation: G1P is activated to UDP-glucose by UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase.
- Glycogen Synthesis: Glycogen synthase adds glucose units to glycogen via α-1,4-glycosidic bonds.
- Branching: Branching enzyme forms α-1,6-linked branches for structure and solubility.
-
Glycogenolysis (Breakdown of Glycogen)
- Purpose: Breaks down glycogen into glucose for energy.
-
Key Steps:
- Glycogen to G1P: Glycogen phosphorylase cleaves α-1,4 bonds, releasing glucose-1-phosphate.
- Debranching: Debranching enzyme removes α-1,6 branches, releasing glucose.
- G1P to G6P: G1P is converted to G6P by phosphoglucomutase.
- Glucose Release: In the liver, glucose-6-phosphatase converts G6P to free glucose, released into the blood.
Glycogen Storage Diseases (GSD)
- GSDs result from enzyme deficiencies affecting glycogen metabolism, causing abnormal glycogen accumulation or structure.
-
GSD Type I (Von Gierke Disease)
- Enzyme Deficiency: Glucose-6-phosphatase
- Symptoms: Hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, growth retardation, lactic acidosis
- Affected Tissues: Liver and kidneys
-
GSD Type II (Pompe Disease)
- Enzyme Deficiency: Lysosomal acid α-glucosidase
- Symptoms: Muscle weakness, cardiomegaly, respiratory issues
- Affected Tissues: Muscles and heart
-
GSD Type III (Cori Disease)
- Enzyme Deficiency: Debranching enzyme
- Symptoms: Hepatomegaly, muscle weakness, hypoglycemia
- Affected Tissues: Liver, muscles
Advertisements