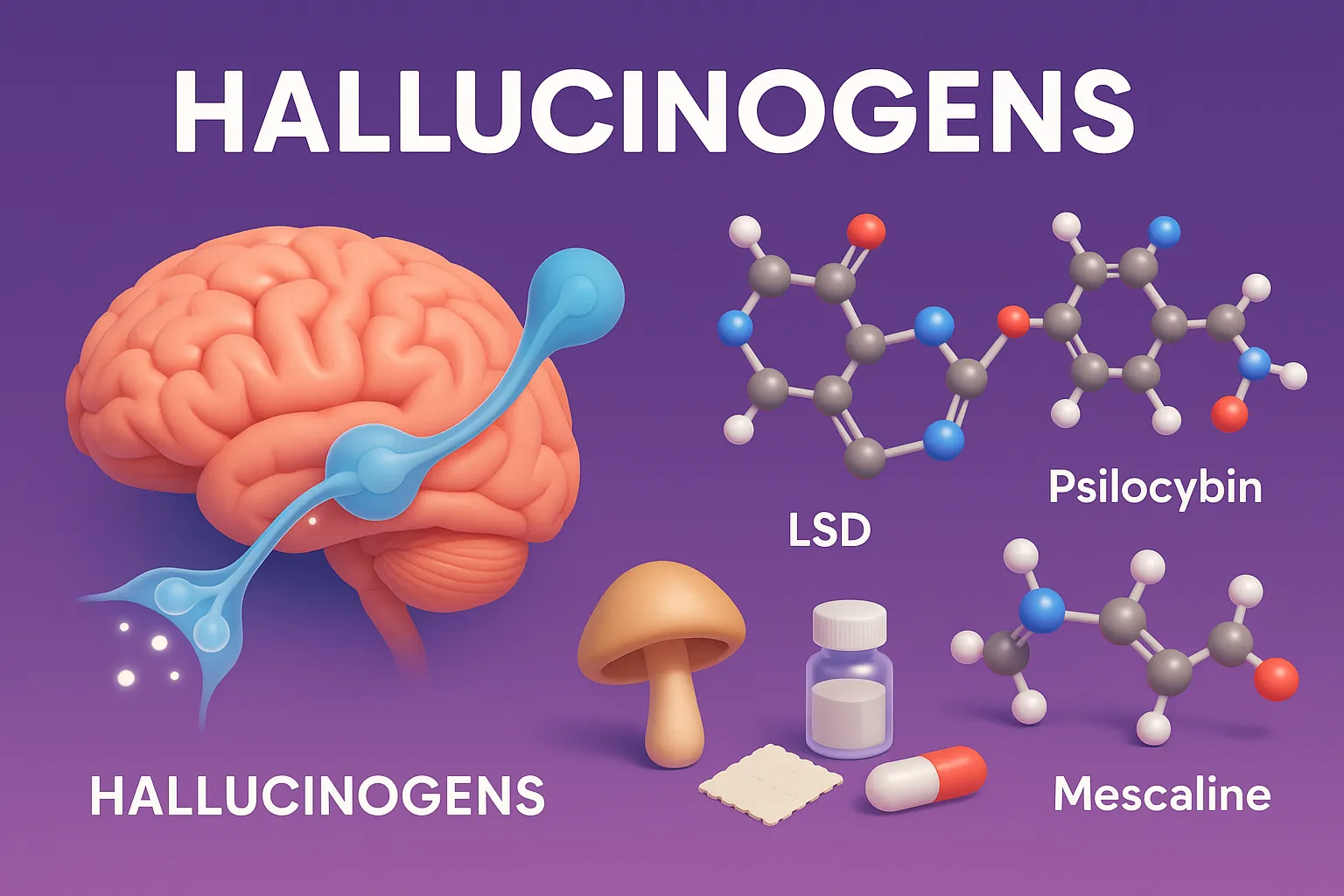
Hallucinogens are psychoactive drugs that alter perception, mood, and thought, often causing hallucinations.
Definition of Hallucinogens:
- Substances that cause altered perception, hallucinations, and mood changes.
Classification of Hallucinogens:

-
Classical (Psychedelics)
- Primarily serotonin 5-HT2A receptor agonists
- Examples:
- Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)
- Psilocybin (magic mushrooms)
- Mescaline (peyote cactus)
- DMT (dimethyltryptamine)
-
Dissociative
- Antagonists of NMDA glutamate receptors
- Produce detachment from body and surroundings
- Examples:
- Ketamine
- Phencyclidine (PCP)
-
Deliriants
- Block muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
- Cause confusion and realistic hallucinations
- Examples:
- Scopolamine
- Atropine
- Datura species
Mechanism of Action:
- Classical hallucinogens stimulate serotonin receptors, especially 5-HT2A, altering sensory processing.
- Dissociatives block NMDA receptors, affecting glutamate neurotransmission.
- Deliriants inhibit acetylcholine, disrupting normal brain signaling.
Effects:
- Visual and auditory hallucinations
- Altered time perception
- Euphoria or dysphoria
- Synesthesia (mixing of senses)
Adverse Effects:
- Hallucinations, flashbacks, panic attacks, psychosis
- Ketamine/PCP: dissociation, aggression, neurotoxicity
- Minimal physical dependence, but risk of psychological addiction
Therapeutic Investigations (Experimental):
- Psilocybin, MDMA being explored for depression, PTSD
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos